October 4, 2023 | Trends in plant science | Source |
Introduction: Low-carbon agriculture is crucial for addressing climate change, and rhizosphere exudates play a key role in managing the nitrogen (N) cycle in soils and water. These exudates, which are small chemical signals released by plants and microorganisms, help reduce nitrogen loss and pollution. A research team based in Foshan University in China collaborated with other researchers from China and Australia in conducting a research review on biological nitrification inhibitors (BNIs), denitrification inhibitors (BDIs), and denitrification promoters (BDPs) in terms of controling greenhouse gas emissions and N runoff.
Key findings: BNIs and BDIs help reduce N2O emissions and improve nitrogen use efficiency, while BDPs enhance nitrogen removal in aquatic systems. Implementing plants with enhanced BNI/BDI/BDP traits, developing green fertilizers, and using bioagents for water purification are promising strategies. Genetic engineering and breeding could further optimize these traits, but careful consideration is needed to avoid negative effects on plant growth and soil microorganisms.
Rhizosphere exudates also impact microbial communities and can contribute to carbon sequestration, aiding in carbon neutrality. However, more research is needed to understand their effects across different conditions and to make them cost-effective. Overall, improving our knowledge of rhizosphere exudates will support low-carbon agriculture and environmental sustainability.
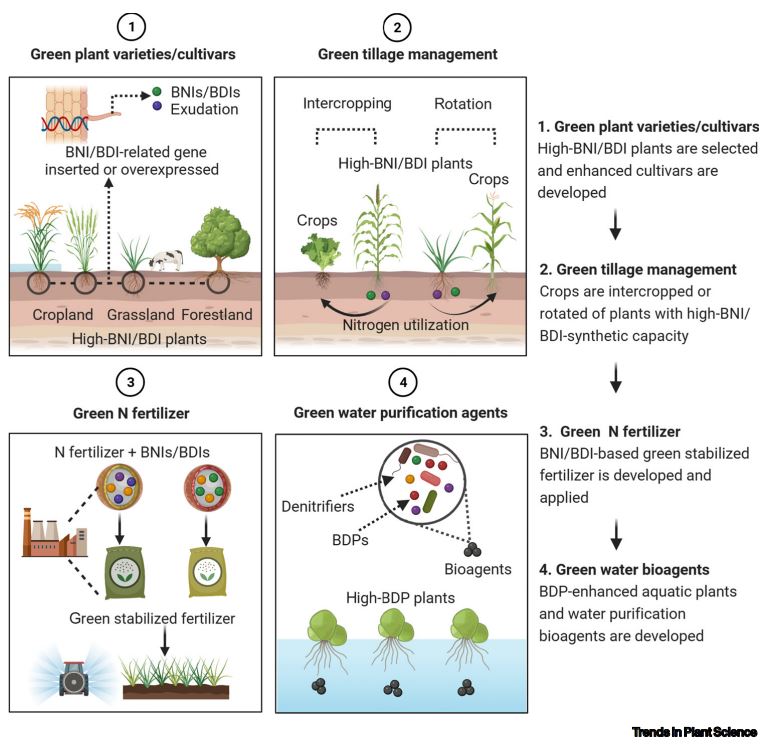
Figure | Application scenarios of small-molecule rhizosphere exudates to achieve low-carbon agriculture. 1) High-biological nitrification inhibition (BNI)/biological denitrification inhibition (BDI) plant varieties are selected, and BNI/BDI-enhanced green crop cultivars can be developed via genetic engineering to optimize the synthesis and secretion of rhizosphere exudates; (2) green tillage management involving intercropping or rotation of crops with high-BNI/BDI-synthetic capacity; (3) addition of specific rhizosphere exudates (BNIs and BDIs) as green nitrogen (N)-fertilizer synergists to N fertilizer; (4) when excessive N fertilizer is lost to aquatic environments, rhizosphere secretions can be applied as green water purification agents to remove N from eutrophic water [62], or biological denitrification promotion (BDP)-enhanced aquatic plants can be deployed. These technologies can be applied together to achieve lower carbon emissions.