January 21, 2024 | Global Change Biology | Source |
Introduction: Soils store large amounts of carbon in the subsoil (below 20 cm), where it can remain for centuries or even millennia. This makes subsoil carbon an important target for climate change mitigation. A research team based in Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences in Sweden collaborates with researchers from China, Germany, and the Netherlands in reviewing processes and models that describe how carbon is stored and moves through the soil profile.
Key findings: Key processes influencing subsoil carbon include root growth, microbial decomposition, and movement through the soil, with most models using the diffusion–advection–reaction framework. The study finds that the primary factors affecting carbon profiles are the balance between carbon inputs from roots and decomposition, rather than advective or diffusive transport.
New carbon inputs to the subsoil are generally cycled quickly and may not significantly contribute to long-term climate mitigation. Instead, preserving existing subsoil carbon stocks is crucial, as they have accumulated over centuries to millennia. Effective management should focus on conserving these stocks and reducing the loss of carbon through land-use changes or unsustainable practices.
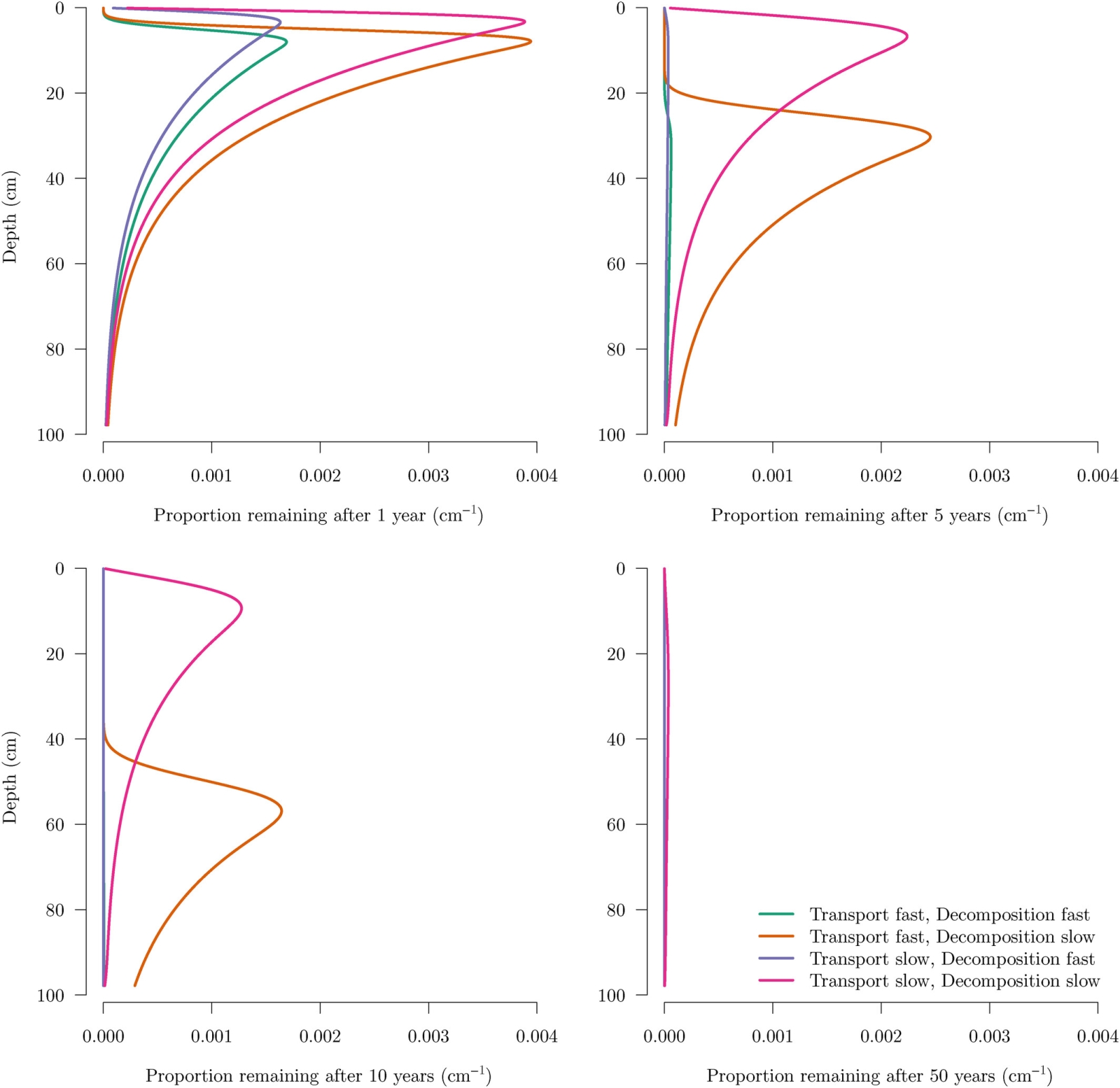
Figure | Proportion of C remaining in a soil profile of an amount of lateral inputs entering the soil at represented by Equation (18) with. After 50 years, most of the carbon that entered at is not present in the soil, even for the scenario with slow transport and decomposition rates.





