September 5, 2023 | Annual Review of Environment and Resources | Source |
Introduction: Soil organic carbon (SOC) is crucial for soil health and ecosystem services, but human activities have led to a significant loss of SOC, impacting carbon storage and increasing greenhouse gas emissions. While efforts to enhance SOC through practices like "4 per 1000" have gained attention, challenges remain in accurately monitoring SOC changes, especially in deeper soils. The review by research team based in Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands, in collaboration with researchers from Kenya, the US, and Australia, emphasizes the importance of improving SOC management and policies to support global climate goals.
Key findings: SOC varies significantly depending on climate, soil types, and land use, with notable changes expected in permafrost, peatland, mangrove, and volcanic ash soils. Land use changes, such as modifying tree cover or managing perennial grasses, can substantially impact SOC storage, but these changes are complex and often uncertain.
Global warming is expected to reduce SOC, particularly in subarctic zones, while root-based inputs to SOC are important but not well understood. Effective SOC management also requires considering erosion, sedimentation, and the balance between aboveground and belowground inputs.
Restoring SOC through better soil management can improve water buffering, which is crucial for agriculture in a changing climate. However, successful SOC transitions require realistic expectations, alignment with national carbon accounting, and collaboration among land users, policymakers, and the private sector.
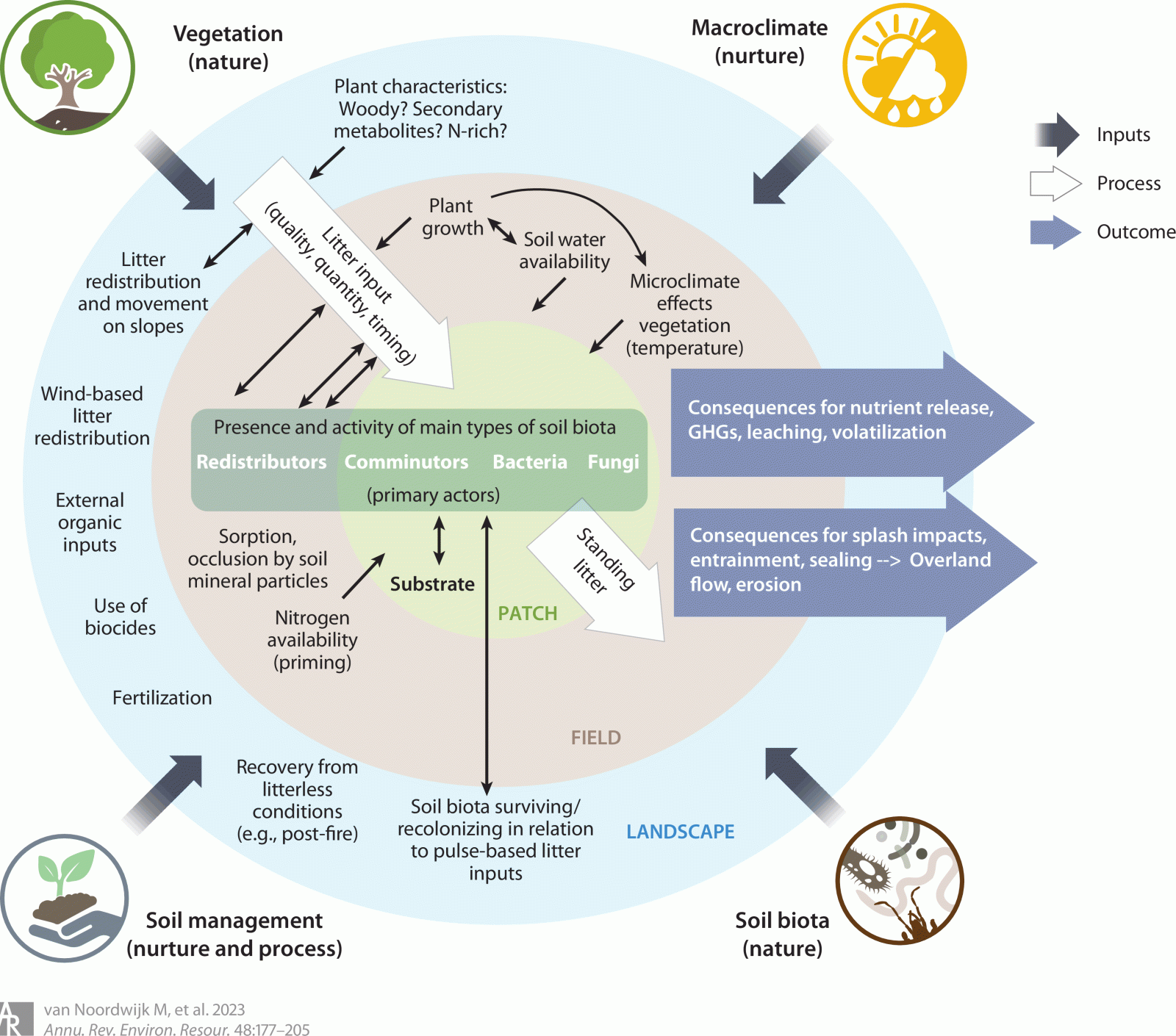
Figure | Vegetation (source of above- and belowground organic inputs), macroclimate (modified by vegetation to the prevailing microclimate), soil management (by farmers) and soil biota (as active agents) interact across landscape, field and patch scale (represented by concentric circles) and influence the input of organic inputs to the soil biota, the rates of decomposition and conversion to other soil C pools and thus the residence time of various pools in the surface litter and soil layers. Abbreviation: GHG, greenhouse gas.





