June 19, 2024 | Nature | Source |
Introduction: A freelance science journalist based in Sydney, Australia reviewed the role of farming in climate change mitigation.
Key findings: Humanity faces two main carbon-related challenges. First, there is an excess of carbon in the atmosphere, largely due to fossil fuel combustion and agriculture, which accounts for over a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions. Second, there is a significant depletion of carbon in the soil, driven by intensive farming practices. Agriculture, although a carbon source, has the potential to become a carbon sink, helping mitigate climate change.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlights soil carbon sequestration in agriculture as one of the most promising strategies to reduce net emissions. Techniques such as no-till farming, cover cropping, and enhanced weathering (adding ground-up silicate rock to soil) can increase soil carbon storage. Agroforestry, integrating trees into farming systems, also contributes to carbon sequestration while providing additional benefits.
Despite its potential, soil carbon sequestration has limitations and challenges, including measurement difficulties and natural variability. However, if implemented effectively, it could significantly reduce atmospheric CO2 levels. The adoption of carbon-positive farming practices is gaining momentum, driven by both environmental concerns and economic incentives like carbon credits. While there is some resistance within farming communities, the impact of climate change on agriculture is prompting a shift towards more sustainable practices.
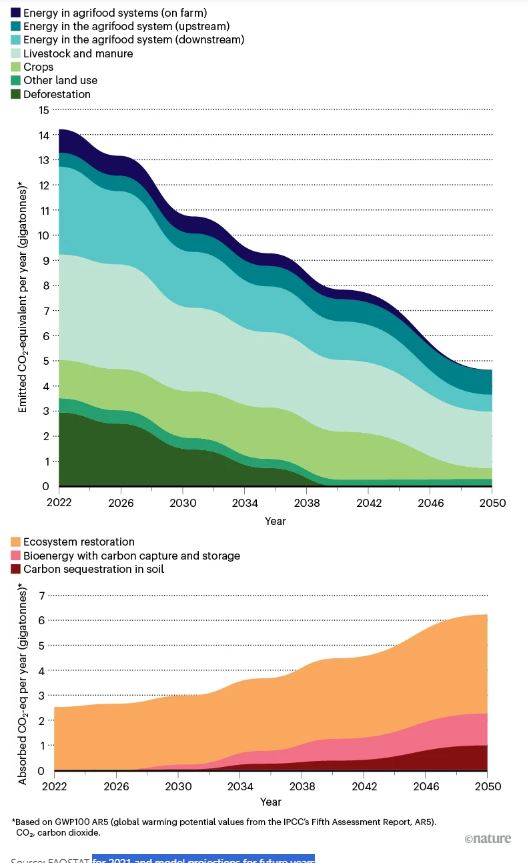
Figure | Green Horizons. The Food and Agriculture Organizations (FAO) of the United Nations unveiled the first instalment of its agrifood roadmap at the COP28 climate meeting in 2023. It hightlighs several carbon-producing domains – particularly for methane – that can be targeted to reduce net emissions from the global agrifood system (top) and that can be used as carbon sinks (bottom).
Source: FAOSTAT for 2021 and model productions for future year