June 25, 2024 | Nature Communications | Source |
Introduction: The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and the European Green Deal aim to reduce pesticide use by 50% by 2030, which may impact agricultural productivity. EU Joint Research Center led research team explores the economic benefits of promoting natural pest control (NPC) through landscape features (LF-NPC) that support beneficial species like predators and parasitoids.
Key findings: The research found that regions with higher LF-NPC potential generally experience positive changes in income and productivity. However, results vary by region due to differences in crops and cost structures. For example, regions growing fodder crops face less revenue loss from reduced pesticides compared to those growing cereals. The study highlights that while higher LF-NPC can reduce yield gaps and improve productivity, the financial impact varies based on local conditions.
The research also notes that LF-NPC is a proxy for the abundance of natural pest controllers, and improving landscape complexity can help mitigate the negative effects of reduced pesticide use. However, the study focuses on a general quantification and does not account for all potential benefits or costs, such as local pest dynamics or redesign costs. It underscores the need for further research to refine these estimates and integrate broader ecological factors. Overall, the study provides valuable insights into the economic advantages of LF-NPC, helping guide future policies and practices in agricultural management.
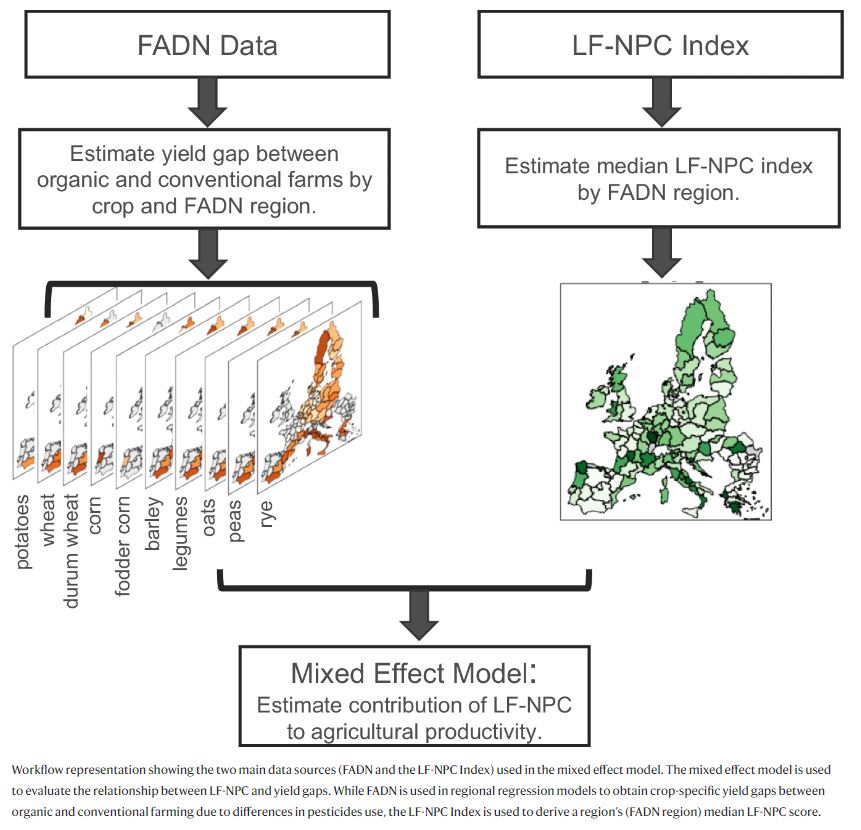
Figure | Schematic workflow to estimate the contribution of LF-NPC potential to agricultural production.