February 24, 2023 | Environmental Chemistry Letters | Source |
Introduction: Climate change drives the need for advanced, carbon-neutral methods to produce materials and fuels. Biomass pyrolysis, the process of heating organic material in the absence of oxygen, is a key focus in this area. This review by international consortium of researchers from UK, Japan, China, Taiwan, and Egypt examines the pyrolysis of algal and lignocellulosic biomass, highlighting product types, upgrading techniques, economic feasibility, and life cycle assessments.
Key findings
The key products from pyrolysis are bio-oil, syngas, and biochar. Upgrading methods include hot vapor filtration, solvent addition, and steam reforming. Economic evaluations show that pyrolysis can be profitable, with factors like feedstock type, temperature, and reaction time affecting product yields. Pyrolysis mechanisms involve breaking bonds and forming new compounds. Biochar can sequester carbon, potentially removing up to 2.75 gigatons of CO2 annually.
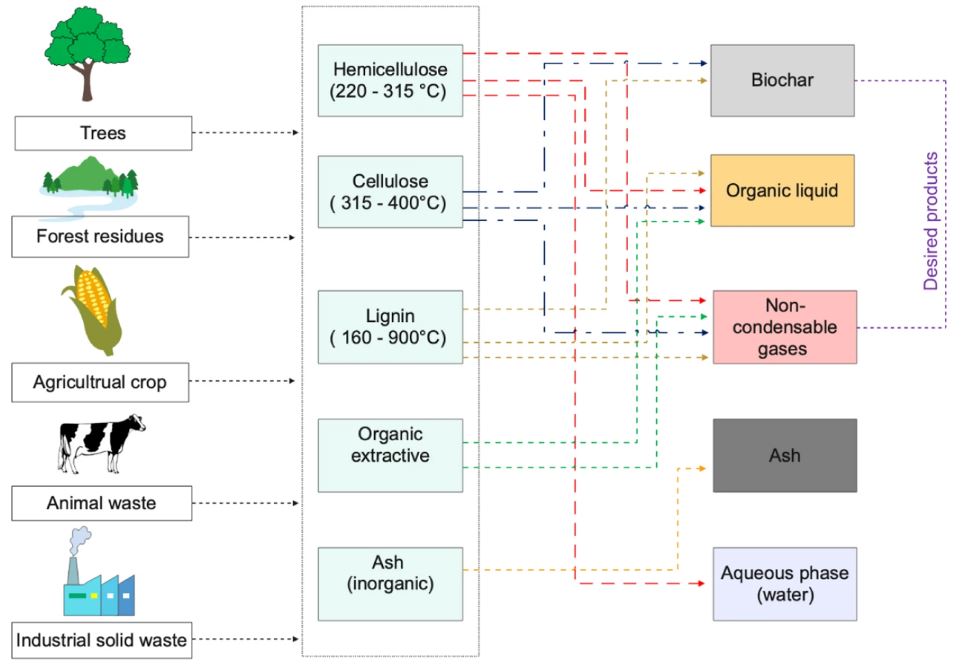
Bio-oil is the primary product from cellulosic biomass, while lignin-rich biomass yields more biochar. Pyrolysis conditions like temperature, heating rate, and residence time crucially influence the product distribution. Higher temperatures increase syngas output but reduce biochar.
Recent life cycle assessments indicate that using waste as feedstock is environmentally beneficial compared to growing energy crops. Pyrolysis is effective for producing sustainable bio-oil and biochar, which can be further refined for advanced materials and chemical recovery.
Figure | Lignocellulosic biomass degradation pathways. Lignocellulosic biomass degrades independently at a wide range of temperatures, producing target products, and byproducts. Therefore, selecting a particular biomass feedstock may have a meaningful impact on the final product yield.