July 13, 2024 | Nature Communications | Source |
Introduction: The on-site conversion of organic waste into biogas can effectively address energy needs and climate change. Existing methods often fail to match biogas supply with demand, leading to inefficiencies. Researchers from China, the US, and UK present an improved community biogas production and distribution system (CBPD) that aims to solve these issues. By analyzing five existing systems, the study introduces mechanisms to adjust biogas flow rates and improve the consumption-to-production ratio. This approach ensures that rural energy needs are met while reducing carbon emissions.
Key findings: The proposed system could significantly reduce China's greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the global 1.5°C climate goal. It also offers practical benefits, such as enhanced manure management and increased biogas use for cooking and agriculture. The study highlights the importance of regional adaptations and improved feedstock collection to optimize biogas production. Upgrading CBPDs in rural areas could reduce fossil fuel reliance and improve waste management. The study calls for further research on policy measures and technical improvements to ensure effective biogas supply and maximize climate benefits. Integrating CBPDs with other renewable energy sources could further enhance their efficiency and contribution to sustainable energy solutions.
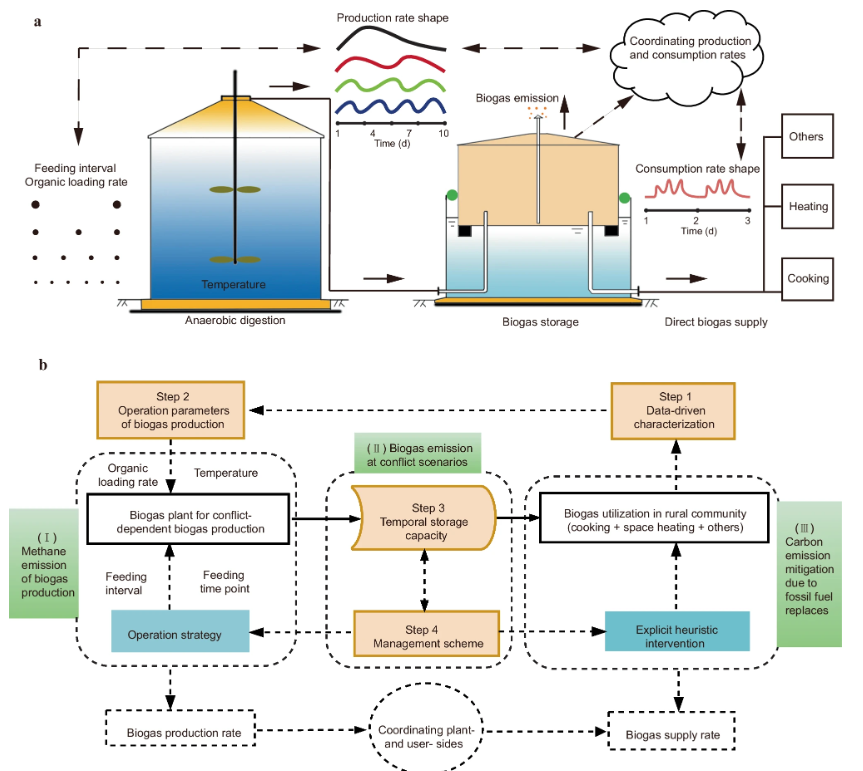
Figure | Upgraded community biogas production and distribution system (CBPD) design. a Schematic diagram of the biogas flow. Biogas losses occur when the temporal redundant biogas exceeds the storage capacity. b Framework to establish an upgraded CBPD for a demand-driven biogas supply. Data on the rural community’s energy consumption is collected to estimate biogas consumption. The dynamically measured biogas supply rate is designed to equal the timely consumption/utilization rate in the community. Parts (I), (II) and (III) are sources of greenhouse gas emission or mitigation. Dotted arrows indicate information flow, and solid arrows indicate biogas flow.





