May 7, 2022 | Environmental Chemistry Letters | Source |
Introduction: Biochar, a recycled material created from organic waste, has diverse applications across various sectors due to its role in climate change mitigation and the circular economy. This review by an international consortium of researchers from Ireland, UK, Japan, Qatar, Egypt, and the US covers biochar's use in several key areas:
Key findings
- Agronomy: Biochar can enhance soil health and crop productivity when used as a fertilizer. It acts as a long-term carbon sink and can improve soil properties, though its effectiveness varies based on feedstock and preparation methods.
- Animal Farming: Adding biochar to animal feed can boost growth, improve gut health, and reduce methane emissions. It also has potential benefits as a litter additive and for managing wastewater.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Biochar can improve biogas production and digestion performance by adsorbing pollutants and enhancing microbial activity. However, more research is needed to optimize its use and understand its effects on large-scale systems.
- Composting: When mixed with compost, biochar can enhance microbial activity and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It can also improve soil quality, though careful management is needed to avoid issues like heavy metal accumulation.
- Environmental Remediation: Biochar can remove pollutants from water and soil, contributing to sustainability goals. Its use must be carefully managed to avoid potential environmental risks associated with its production and disposal.
- Construction and Energy Storage: Biochar can be used in building materials and energy storage systems. It provides benefits like improved insulation and moisture control but requires careful processing to maximize its effectiveness and minimize environmental impact.
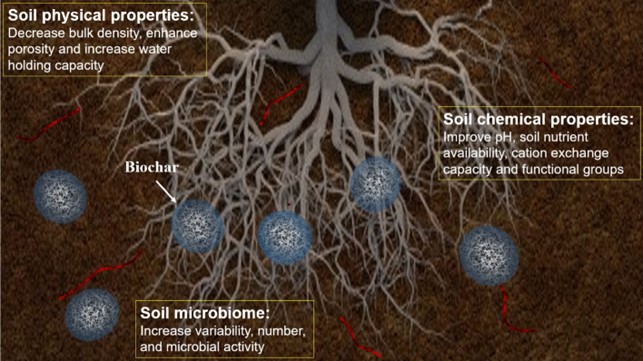
Figure | Biochar has a significant role in improving the chemical, physical, and microbiological properties of soil. Among the chemical properties of soil that can be improved are pH, nutrient availability, cation-exchange capacity and functional groups. Additionally, soil physical properties such as bulk density, porosity, and water holding capacity properties can be improved. Moreover, soil biological properties are enhanced by the addition of a significant amount of bioavailable nutrients, which improve the variety, number, and activity of soil microorganisms.





