May 1, 2023 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | Source |
Introduction: Decarbonizing industries like steelmaking, cement production, and chemicals is challenging due to the limited availability of low-carbon options. Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) is a promising solution, helping reduce carbon emissions in these hard-to-decarbonize sectors. An international consortium of researchers from the US, Denmark, and Republic of Korea examines how CCUS can aid in industrial decarbonization by exploring technical, economic, and social factors.
Key findings:
The specific CCUS reviewed that are applicable to decarbonizing agrifood system include indirect air catpure (such as by photosynthesis), afforestation and forestry, blue carbon and ocean storage, algae culturing, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage. The specific utilizations reviewed that are applicable to agrifood sytems include production of fertilizers, biochar, and bioproducts. The key aspects highted in the review are as listed below.
- Technical and Economic Factors: CCUS involves capturing carbon emissions, transporting them, storing them safely, and utilizing them. Technologies such as direct air capture and various storage methods are discussed.
- Policy and Regulation: Effective policies are crucial for CCUS deployment. Key factors include stable regulations, early site identification, and research funding. Without these, CCUS adoption faces significant barriers.
- International Cooperation: Global efforts are uneven, and developed countries are encouraged to lead. Unilateral policies and international treaties are explored for their effectiveness in encouraging worldwide participation.
- Challenges and Solutions: The review identifies barriers such as high costs and the need for better regulatory frameworks. It suggests policies like grants, subsidies, and carbon pricing to support CCUS
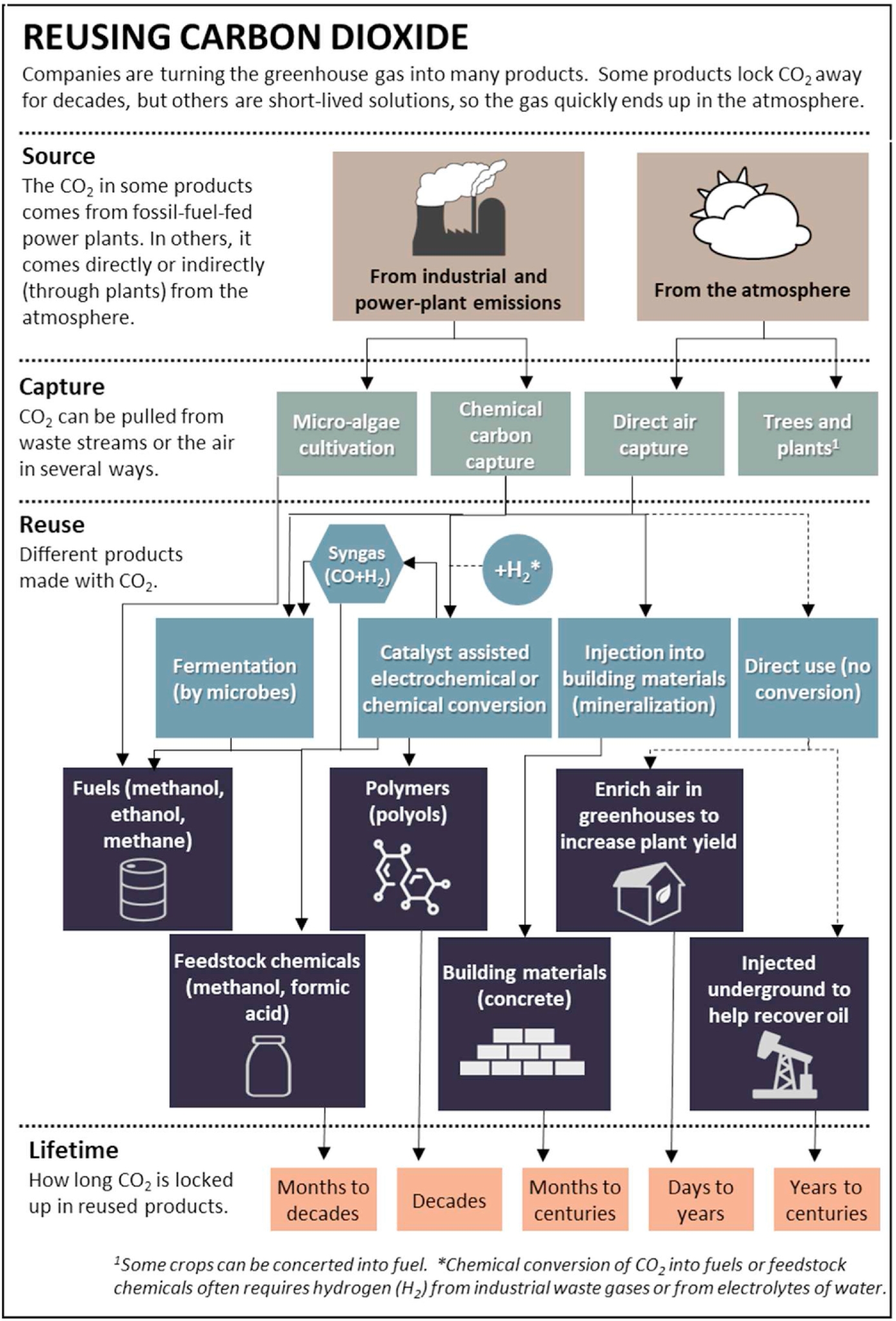
Figure | Conceptualizing carbon capture utilization and storage.





