March 17, 2023 | One Earth | Source |
Introduction: Food waste and wastewater are significant sources of carbon emissions in cities, but they also hold potential for turning waste into valuable resources while reducing emissions. Traditional waste treatment often fails to realize this potential and can cause additional environmental issues. A new approach proposed by researchers based in Princeton University in the US involves using electrochemically engineered microbiomes to convert these waste streams into useful products, offering a more sustainable solution.
Key findings: This framework proposes integrating food and water waste through co-digestion and biofilm-based treatments, coupled with low-cost renewable electricity. By electrifying the microbiomes that process these wastes, we can enhance their efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, biochar, a byproduct of waste, can be used in various applications like stormwater management and wastewater treatment due to its high water retention and ability to support bioreactions. The framework also suggests that using electrochemical processes can help produce valuable chemicals from waste, such as organic acids, which are currently used in niche markets but have potential for broader applications. This approach not only reduces the carbon footprint of waste treatment but also creates economic opportunities by converting waste into high-value products.
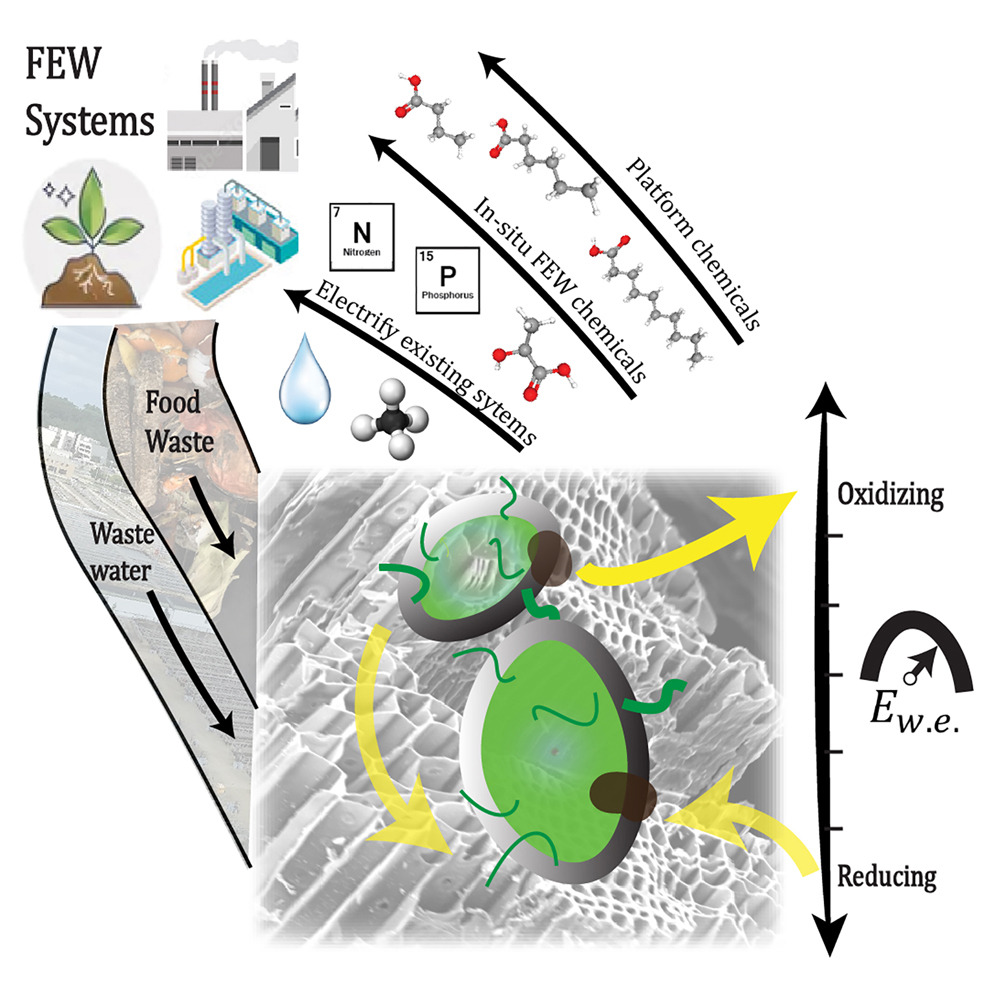
Figure | Technology roadmap for the application of electrochemically engineered microbiomes to enable an urban circular carbon economy.





