March 1, 2023 | Resources, Conservation and Recyling | Source |
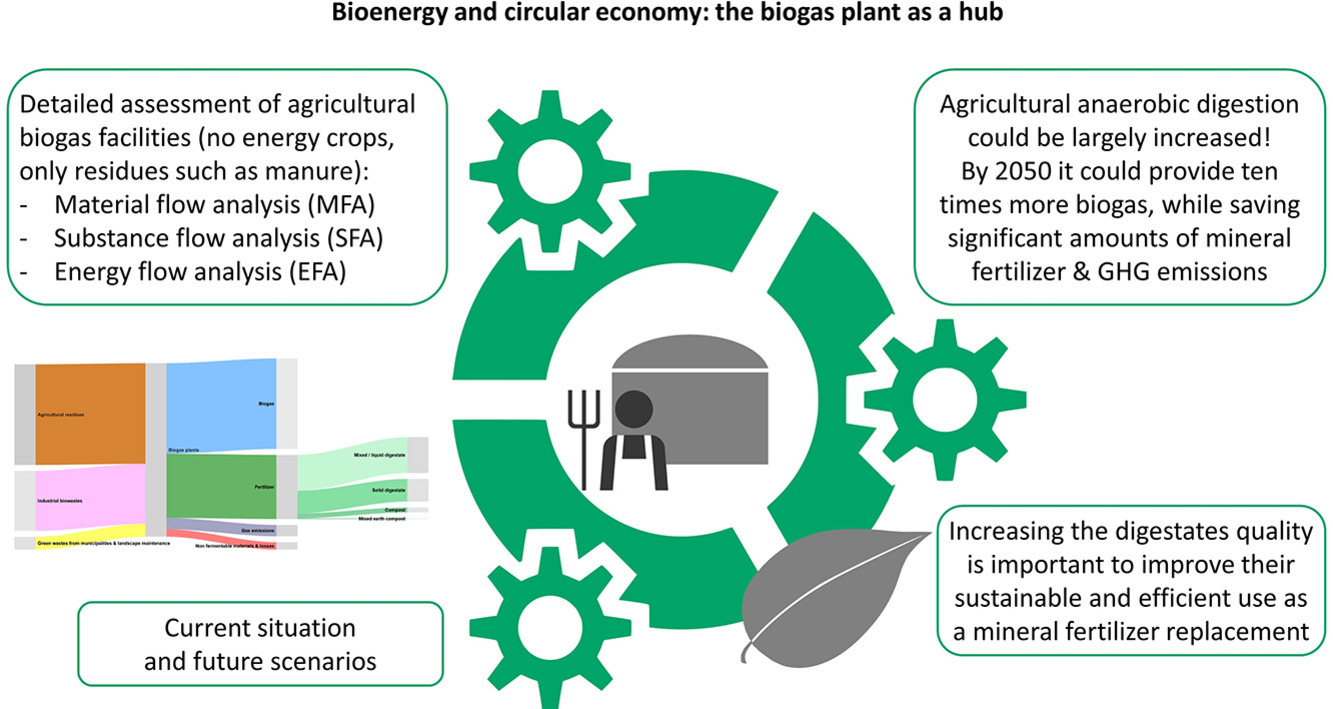
Introduction: Currently, Swiss AD plants produce around 1,300 TJ of biogas annually, which could potentially be increased tenfold by 2050. This expansion could significantly reduce the need for mineral fertilizers and fossil fuels, lowering CO2 emissions by 38 kt annually. The study by researchers from Switzerland focuses on optimizing the use of biomass in agricultural anaerobic digestion (AD) plants in Switzerland, aiming to enhance the circular economy and mitigate climate change.
Key findings: The study highlights that while 47% of the energy in input biomass is converted into biogas, the rest remains in solid and liquid residues. There is a need for better quality data to improve the accuracy of these measurements. The research indicates that agricultural digestates are valuable, providing essential nutrients and improving soil quality. However, their economic value is currently underutilized, partly due to market limitations and the preference for separate fertilizers. The study suggests that Switzerland needs to fully leverage its renewable energy potential, including biogas, to meet climate goals. Policymakers should enhance support for biogas plants and consider technological advancements to increase efficiency. Expanding this approach could also be beneficial if applied on a broader scale and integrated with other biomass uses. Overall, the study underscores the importance of advancing biogas technology to support sustainable agriculture and environmental management.
Graphical Abstract