January 10, 2022 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source |
Introduction: Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a crucial technology at the intersection of waste management, energy production, and land use. An European research team based in University of Limerick in UK assesses the effectiveness of AD in reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions within different decarbonization contexts using life cycle assessment.
Key findings: Results show that while AD can effectively manage residual food waste and manures, alternative strategies like food waste prevention, animal feed diversion, solar electricity generation, and afforestation offer more significant GHG reductions. As energy systems decarbonize, AD's role shifts from transport fuel to large-scale biogas combustion, especially with bioenergy carbon capture and storage (BECCS). However, maximizing GHG mitigation requires prioritizing waste prevention, renewable energy technologies, and nature-based solutions like afforestation. AD remains valuable, especially for residual waste management and short-term clean transport fuel, but should be part of a broader strategy for achieving climate neutrality.
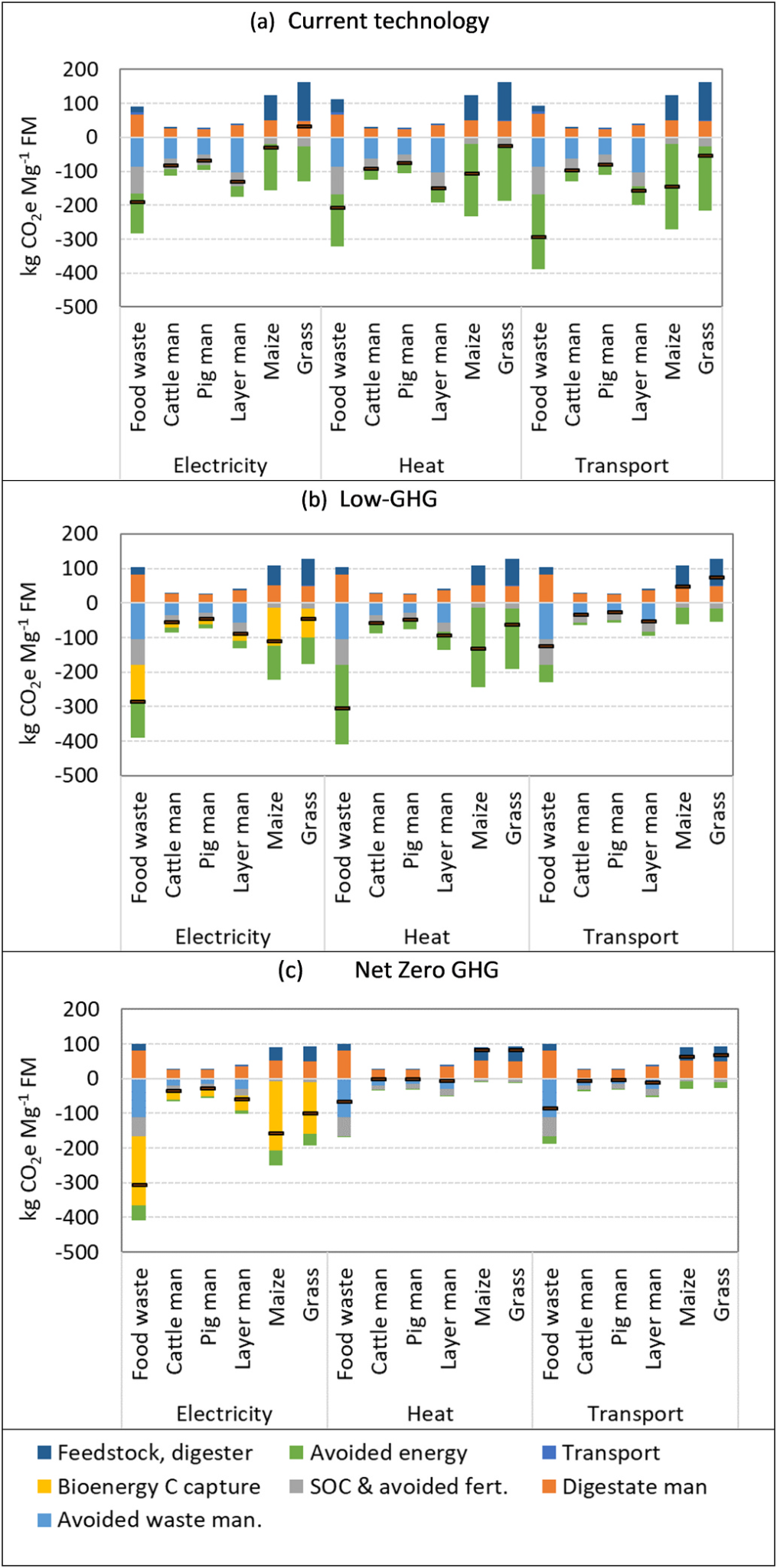
Figure | Global warming potential balance of anaerobic digestion of different feedstocks under different end uses of the biomethane (for electricity generation, heat production or as a transport fuel), and under different contexts –CURRENT technology (top), LOW-GHG (middle), net zero (NZ-) GHG (bottom). The net balance represents sum of emissions from incurred processes (e.g.transport of feedstock, fugitive and combustion emissions from digestion, emissions from digestate management) minus: (i) credits (avoided emissions) from avoided waste management, avoided synthetic fertiliser production and use, and avoided energy carriers; (ii) soil organic carbon storage (SOC) associated with digestate application; (iii) bioenergy carbon capture & storage. Carbon opportunity costs of land use are excluded here for crop feedstocks.





