April 30, 2024 | Trends in Food Science & Technology | Source |
Introduction: A team of researchers from India, UK, and Belgium examines how nonthermal processing technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) can reduce the carbon footprint in food production, promoting sustainability.
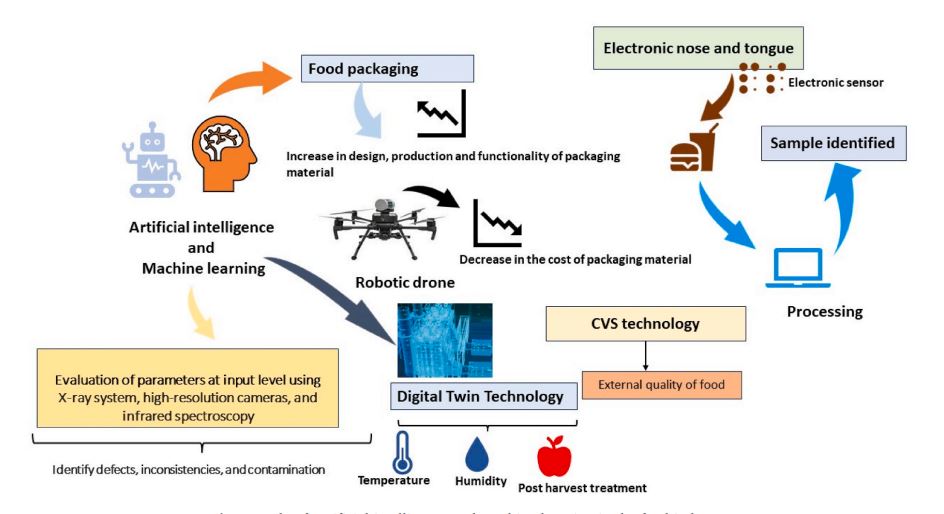
Key findings: Traditional food processing often requires significant energy and water use, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, emerging nonthermal technologies, such as high-pressure processing, pulsed electric fields, and cold plasma, offer alternatives that use less energy and water. These methods effectively inactivate harmful microorganisms and extend the shelf life of food while preserving its nutritional quality. AI technologies, including digital twins and electronic sensors, further optimize these processes by monitoring food quality and enhancing efficiency. By integrating AI with nonthermal techniques, food production can become more sustainable, minimizing environmental impact and aligning with global sustainability goals. By adopting these technologies, the industry can contribute to a circular bioeconomy, ensuring food safety while reducing resource consumption and emissions. This shift is crucial for meeting the growing demands of a sustainable and climate-resilient food system.
Figure | Role of artificial intelligence and Machine learning in the food industry.