September 28, 2023 | Nature Climate Change | Source |
Introduction: Led by Nature Conservancy, an international research consortium of researchers from the US, France, Brazil, and Zimbabwei defines agroforestry as a natural climate solution (AF-NCS) that involves integrating trees into agricultural landscapes to enhance carbon storage without compromising food production or biodiversity. The research consortium helps to identify priority research areas to accelerate the expansion of agroforestry as a natural climate solution.
Key findings: Agroforestry has significant potential to mitigate climate change, with estimated carbon sequestration up to 0.31 Pg C per year, comparable to reforestation. However, its exact benefits are difficult to track and measure. Efforts to estimate agroforestry’s carbon impact mainly focus on woody biomass and soil carbon, though challenges remain due to variability across studies. Other factors, like litter and methane emissions, must also be considered to assess full mitigation potential. Monitoring agroforestry accurately requires advanced technologies like high-resolution remote sensing, but this comes with technical and financial hurdles. Regional customization of monitoring systems might be necessary, while a global agroforestry tracking system could offer broader insights.
Although agroforestry has been recognized in many national climate commitments, substantial opportunity for expansion remains, especially in more developed countries. Expanding agroforestry adoption, particularly in mechanized farming systems, could increase carbon storage and biodiversity. Overcoming challenges such as complex management and delayed returns requires research and policy support.
Effective AF-NCS implementation depends on integrating agroforestry into monitoring systems, incentivizing adoption, and ensuring agroforestry practices are promoted in both policy and practice. Addressing barriers such as land tenure, market access, and technical knowledge will be critical for farmers to adopt agroforestry and realize its climate benefits.
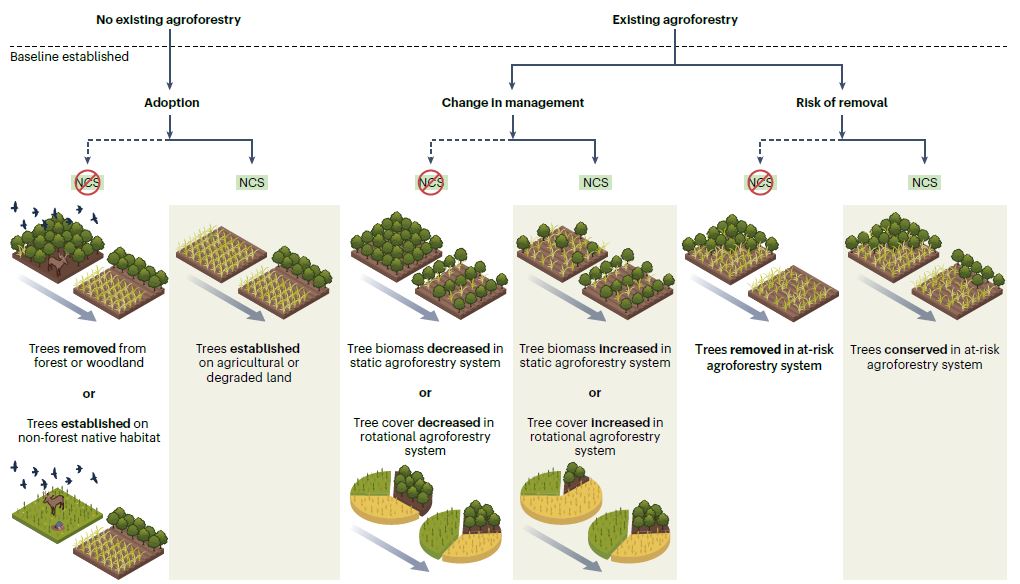
Figure | Land-use change and carbon outcomes determine whether agroforestry is an NCS. If agroforestry does not exist before the baseline, then agroforestry adoption serves as an NCS when it increases woody and soil carbon storage without impacting biodiversity (left). If agroforestry exists at the time of baseline establishment, changing agroforestry management can serve as an NCS if it increases tree biomass or proportional tree cover in static or rotational agroforestry systems, thus increasing carbon storage (middle). Alternatively, conservation of some or all trees can serve as an NCS if those trees would have been removed under business-as-usual conditions, such that their maintenance leads to avoided emissions (right). Figure adapted from image by Vin Reed.