Managing tree-crops for climate mitigation. An economic evaluation trading-off carbon sequestration with market goods
July 1, 2021 | Sustainable Production and Consumption | Source |
Introduction: Climate change considerations needs to be integrated into circular economy by having consumers pay for nature-based solutions employed in the production of agricultural products. Researchers from Panteion University and Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Greece explore how fruit tree cultivation can contribute to CO2 sequestration and estimates the economic value of this ecosystem service.
Key findings: Using a survey-based method that gauges consumers' willingness to pay for eco-labeled products such as olive grown with carbon sequestration methods, the study estimates that around €1,200 per hectare can be generated for adopting cultivation methods that maximize carbon sequestration.This could incentivize farmers to adopt sustainable practices, benefiting rural economic, environmental, and social sustainability. The findings may also influence upcoming EU policies, such as carbon farming schemes, and encourage voluntary CO2 markets.
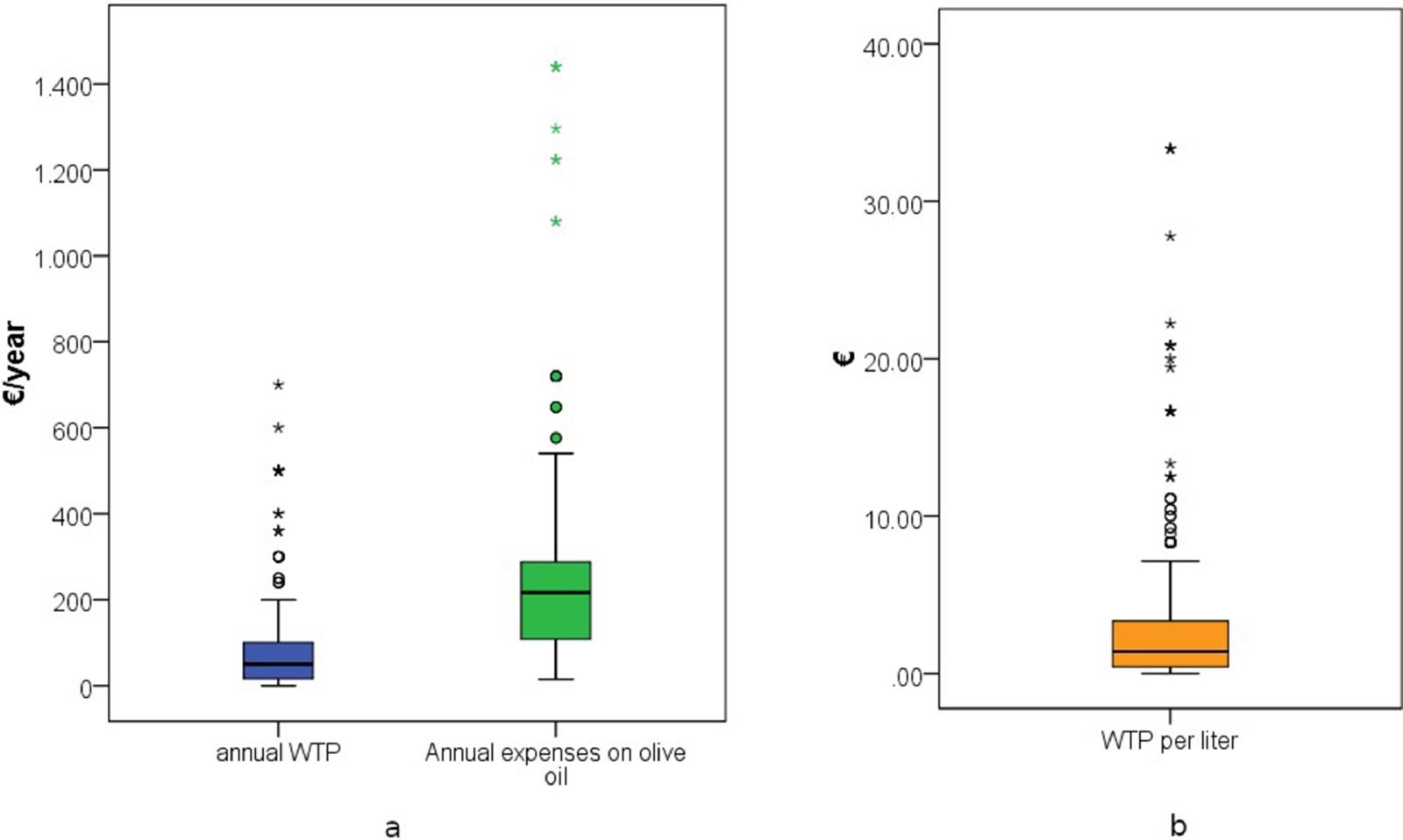
Figure | Box plots of (a) annual willingness to pay (WTP) for certified olive oil in comparison to the actual annual expenditure on olive oil, and (b) WTP per liter of actual consumption
Viewed Articles
July 1, 2021 | Sustainable Production and Consumption | Source | Introduction: Climate change considerations needs to be integrated into circular economy by having consumers pay for nature-based solut
Read More
December, 2024 | Environmental and Sustainability Indicators | Source | Introduction: Agroforestry offers a cost-effective solution for restoring degraded mountain lands by stabilizing soil, reducing
January 2, 2023 | Nature Ecology & Evolution | Source | Introduction: Indonesia, the world’s largest mangrove-rich country, has set an ambitious goal to rehabilitate 600,000 hectares of mangroves by 2
May, 2023 | Forest Policy and Economics | Source | Introduction: Climate-smart agroforestry (CSAF) practices offer integrated solutions to climate change, food security, and environmental degradation,
August, 2023 | Ecosystem Services | Source | Introduction: Agricultural intensification in India threatens ecosystem sustainability, with agroforestry identified as a key strategy to mitigate these i
March 21, 2024 | npj Ocean Sustain | Source | Introduction: Climate change significantly affects marine ecosystems, exacerbated by overfishing and habitat degradation, weakening the ocean's capac






