Coupled coordination and pathway analysis of food security and carbon emission efficiency under climate-smart agriculture orientation
October 20, 2024 | Science of The Total Environment | Source |
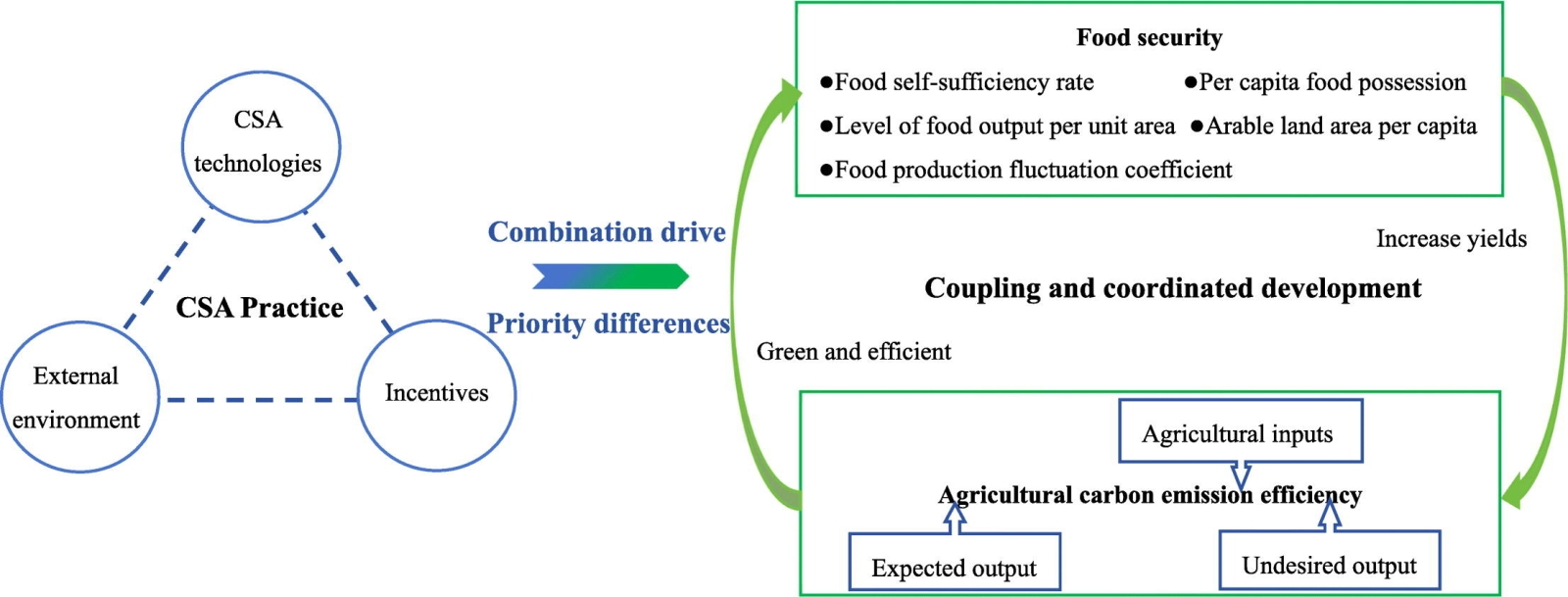
Introduction: Researchers from Beijing Institute of Technology examine and compare the coordination between the two objectives of food security and agricultural carbon emission reduction through diverse configurations of climate smart agricultural (CSA) practices across 31 Chinese provinces from 2010 to 2021, using a coupled coordination model and dynamic qualitative comparative analysis (dynamic QCA).
Key findings: The configurations in CSA for different provinces are tailored to differing regional priorities, as well as diverse socioeconomic and ecological context. While some emphasize on water-saving irrigation with prioirty placed on food security, some emphasize on no-till farming with prioirty placed on emission reduction. The study suggests dry southwest regions to embrace no-till farming; water-scarce areas to adopt water-saving irrigation; the northeast region to adopt straw returning to fields. Applicable to all regions, there is a need to strengthen farmer training, policy guidance, and environmental education in promoting sustainable production practices. Governments must establish and refine agricultural ecological compensation mechanisms, adjust subsidy policies, and incentivize farmers for adopting eco-friendly technologies.
Graphical abstract:
Viewed Articles
October 20, 2024 | Science of The Total Environment | Source | Introduction: Researchers from Beijing Institute of Technology examine and compare the coordination between the two objectives of food se
Read More
June 24, 2024 | Humanities and Social Sciences Communications | Introduction: Digital inclusive finance is widely promoted as an enabler of green transitions, yet its environmental impacts in agricul
April 29, 2021 | Environmental Research Letters | Source | Introduction: Researchers from the University of Freiburg and University of Kassel (Germany), together with the Vienna University of Economi
January 3, 2024 | Nature Communications | Source | Introduction: Conventional intensive farming boosts yields but also drives GHG emissions, soil degradation, and climate vulnerability, especially in
February 28, 2021 | Global Change Biology | Source | Introduction: Mangroves significantly contribute to global climate mitigation by storing substantial carbon, yet their continuous loss poses major
October 20, 2022 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source | Introduction: While organic livestock systems are often hailed as environmentally friendly, their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and carbon






