April 24, 2024 | Science Advances | Source |
Introduction: Short-term studies suggest that plant diversity improves ecosystem resilience, particularly against drought, presenting a potential nature-based solution for climate change. However, it's unclear if these benefits persist long-term. In this study by researchers from Japan, China, Canada and Switzerland, 57 years of data from Canadian dryland forests were analyzed, showing a 1.3% per decade decline in productivity, linked to rising temperatures and decreasing water availability.
Key findings: Notably, increasing tree functional diversity boosted productivity by 13%. While nature-based solutions like reforestation alone aren't enough to mitigate climate change, their effectiveness can be enhanced by promoting functional diversity in forest management strategies.
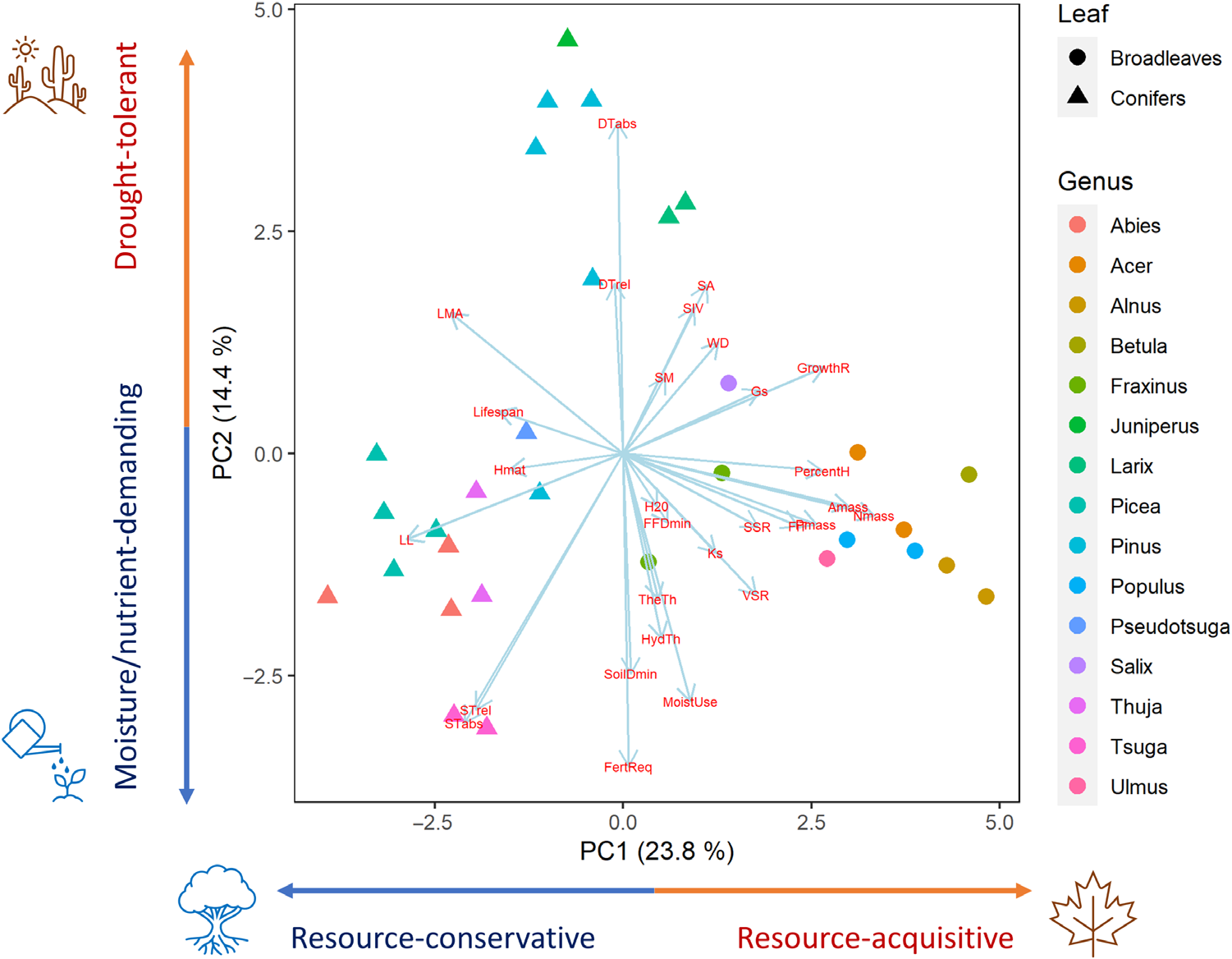
Figure | A result of the principal components analysis showing each tree species and functional trait. The first axis (PC1) represents traits associated with resource-acquisitive (positive PC1) versus resource-conservative strategies (negative PC1), while the second axis (PC2) stands for traits associated with environmental tolerance: drought tolerance (positive PC2) and resource requirements such as moisture and fertility (negative PC2). Nmass, leaf nitrogen content per leaf dry mass; Pmass, leaf phosphorus content per leaf dry mass; Amass, maximum CO2 assimilation rate per unit dry mass; Ks, sapwood-specific hydraulic conductivity; Gs, stomatal conductance; LMA, leaf mass per area; LL, leaf longevity; WD, wood density; DT abs, absolute drought tolerance; STabs, absolute shade tolerance; HydTh, hydric threshold on the data [based on climate moisture index (CMI)]; TheTh, thermophilic threshold on the data [based on mean annual temperature (MAT)]; GrowthR, relative growth rate; H20, height at 20 years, maximum (meters); Hmat, height, mature (meters); PercentH, percent height 20 years divided by mature (how much % grows when 20; years); Lifespan, tree lifespan; Resprout, resprout ability; DT rel, relative drought tolerance; STrel, relative shade tolerance; FertReq, relative fertility requirement; FiT, relative fire tolerance; FFDmin, frost-free days, minimum; MoistUse, moisture use ability; SoilDmin, root depth (minimum depth of soil required for good growth, centimeters); SA, seed abundance; SM, seed mass (milligrams); SSR, seed spread rate; SlV, seedling vigor; VSR, vegetative spread rate (see also table S3).





