March 17, 2021 | Nature | Source |
Introduction: The ocean is crucial for its biodiversity, food supply, and carbon dioxide absorption. Marine protected areas (MPAs) are essential for restoring ocean health, but only 2.7% of the ocean is currently highly protected, primarily due to conflicts with fishing and other activities. To improve this situation, a global research team from US, France, Canada, Germany and others developed a new framework to identify the best locations for establishing highly protected MPAs, which would maximize benefits.
Key findings: The study results reveal that expanding ocean protection could provide three key advantages: preserving marine life, boosting fishery yields, and maintaining marine carbon stocks at risk from human activities. The study highlights that many coastal nations, including the U.S., have critical areas that could contribute significantly to these objectives. A globally coordinated approach to MPAs could be nearly twice as effective as national efforts alone. This framework offers valuable guidance for shaping national marine plans and setting global conservation, food security, and climate action targets.
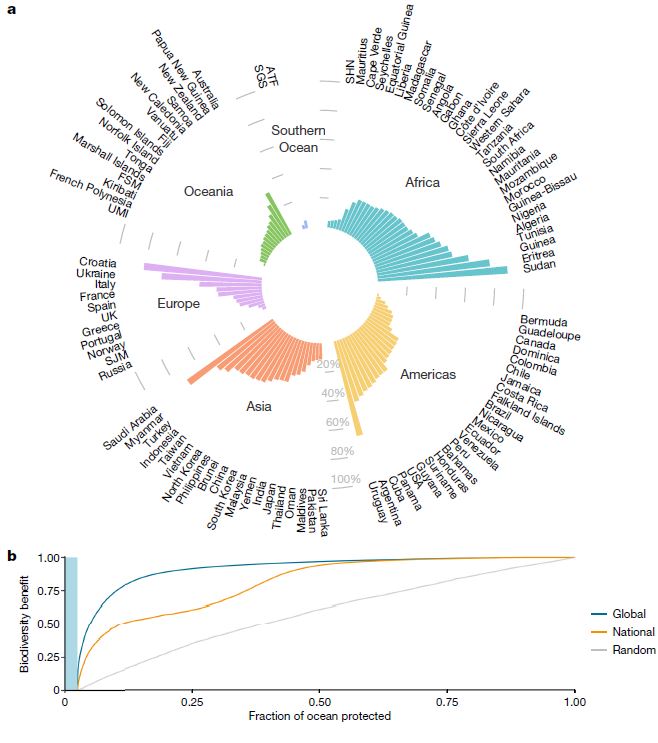
Figure | National contributions to biodiversity conservation and coordinated implementation.
a, Fraction of nations’ EEZs in the top 10% of priority areas for global marine biodiversity conservation. Shown here are the 100 countries or territories with the largest contributions towards achieving the maximum possible biodiversity benefit. Values are in addition to current protection.
b, Cumulative biodiversity conservation benefit from implementing a globally coordinated MPA expansion according to global priorities (blue), national priorities (orange), and random placement (grey; 100 random sets). The blue bar denotes the current 2.7% of the global ocean that is included in fully protected areas. ATF, French Southern Territories; FSM, Federated States of Micronesia; SGS, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; SHN, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; SJM, Svalbard and Jan Mayen; UMI, United States Minor Outlying Islands.