June 1, 2022 | Ecosystem Services | Source |
Introduction: Coastal wetlands are crucial for capturing carbon dioxide and offering various ecosystem services. The research conducted jointly by scientists from the University of Queensland and the James Cook University in Australia evaluated the economic feasibility of restoring these wetlands in Queensland, Australia, as a method for climate change mitigation. The study examined the impact of reintroducing tidal flows to areas previously used for agriculture.
Key findings: The findings indicate that restoring 5,046 hectares of wetlands could potentially reduce carbon dioxide emissions by about 221,000 tons annually. Under the current carbon price, 67% of the restoration area would be financially viable, with this figure rising to 90% if the carbon price were increased.
In addition to carbon sequestration, wetland restoration offers benefits such as enhanced biodiversity, improved water quality and avoided emissions from land conversion to agricultural cultivation. Combining these ecosystem services with carbon credits increases the overall profitability of restoration projects. By selecting sites based on cost-effectiveness and the additional benefits they provide, significant environmental and economic gains can be achieved.
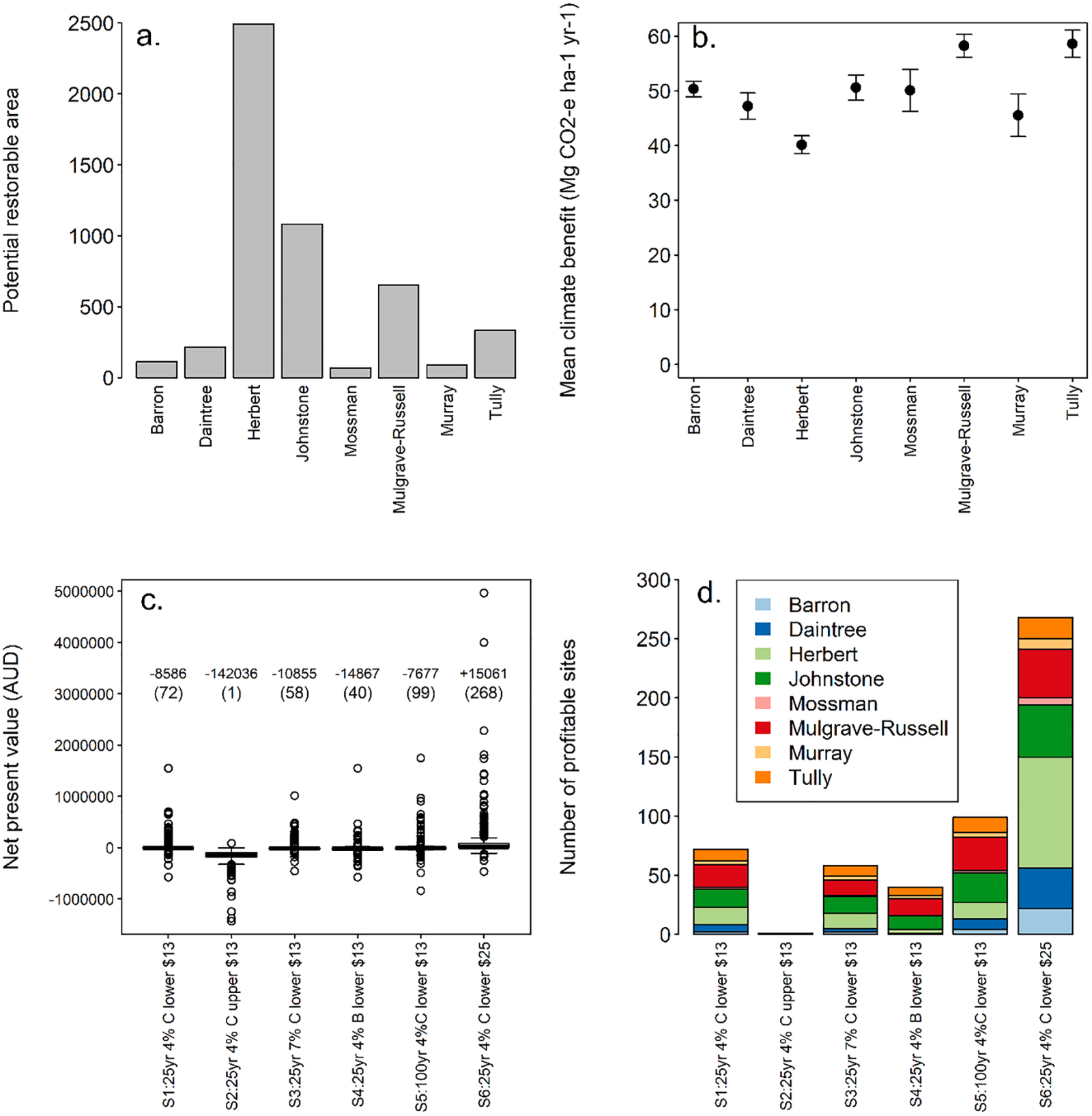
Figure | (a) Restoration opportunity and (b) mean climate benefit with standard error bars across the Wet Tropics catchments, (c) range of net present value (NPV) at restoration sites represented as box and whisker plots with minimum, quartiles, median, and maximum for different NPV scenarios (median values reported), and (d) number of profitable sites per catchment for different NPV scenarios (25 or 100 years, 4 or 7% discount rate, conventional [C] or best [B] farm practice, lower or upper restoration cost; $13 or $25 carbon price).





