June, 2024 | Sustainable Production and Consumption | Source |
Introduction: As the world's largest producer (15.4%) and consumer (21.4%) of rice, China faces the critical challenge of balancing rice yield and soil health while increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) and reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Straw returning is a promising practice for increasing SOC accumulation in rice cropping systems but has been associated with a 60% increase in CH‚āĄ emissions in China. Despite its potential, national-scale studies on optimal straw return rates to maximize yields, increase SOC, and mitigate GHG emissions are limited. This study, led by researchers from the Chinese Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, used the Dynamic Nitrogen and Carbon Model (DNDC) with county-level meteorological, soil, and field management data to simulate the effects of different straw returning rates on yield, SOC, and GHG emissions in China from 2010 to 2022, with the aim of identifying region-specific strategies that balance agricultural productivity with environmental sustainability.
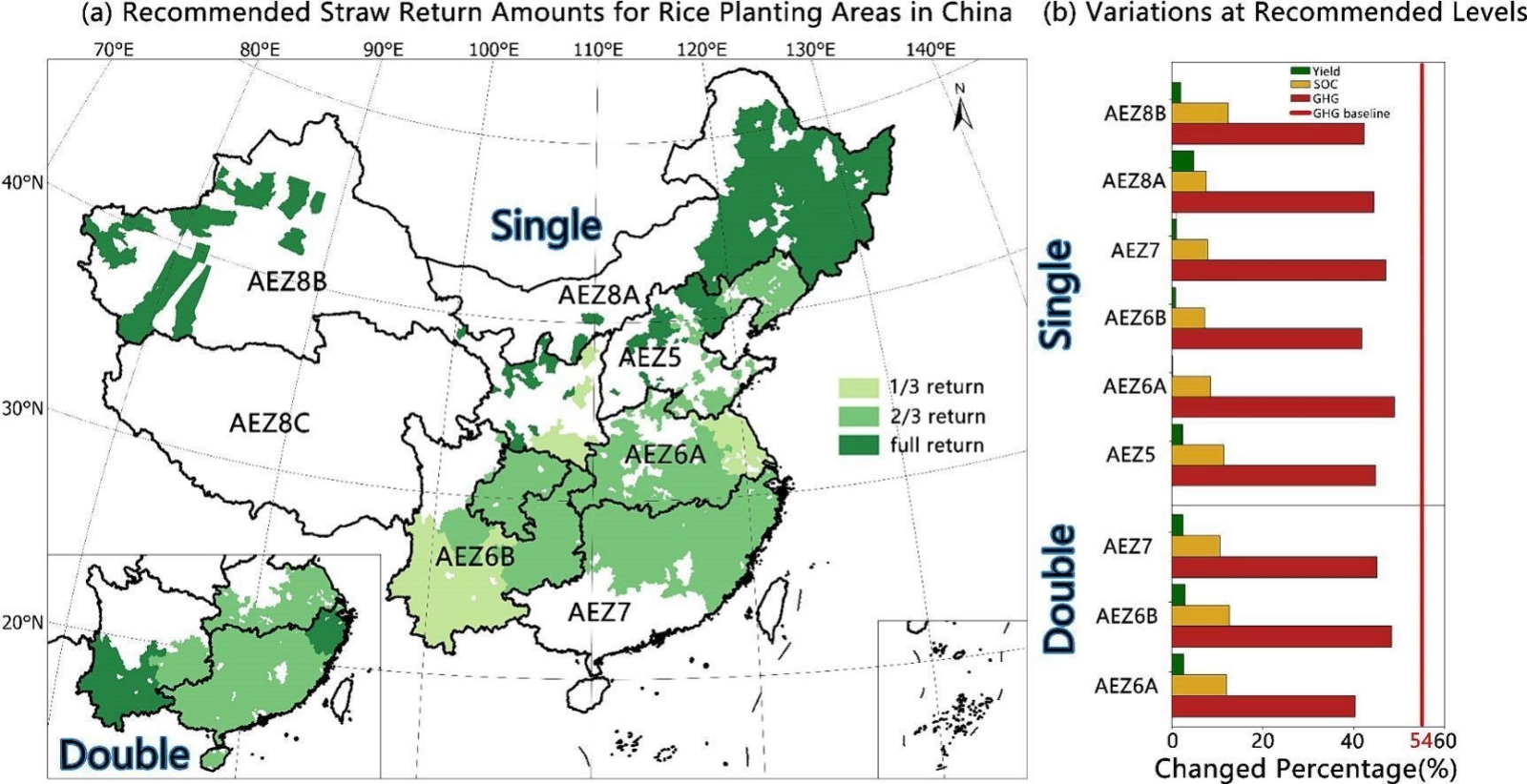
Key findings: This study analyzed rice production in 1,852 counties in China, covering single and double cropping systems in four agro-ecological zones. Using high-precision meteorological (ERA5) and soil data, together with regional farming practices, the researchers simulated yields, soil carbon changes and greenhouse gas emissions. Straw return practices were evaluated for their impact on rice yield, SOC content and GHG emissions using the DNDC model for different incorporation rates (1/3, 2/3 and full straw).
The results showed that straw returning significantly improved rice yields, with yield increases of up to 3.26% for single-crop rice and up to 5.95% for late double-crop rice under full incorporation, while SOC levels improved nationally by 3.88%, 7.75% and 11.65% for the respective rates, with diminishing returns in areas with high initial SOC. Northeast China had the highest yield and SOC gains due to favorable cooler temperatures and soil conditions. However, these benefits came with trade-offs as GHG emissions, particularly methane, increased by 23.32%, 43.50% and 61.48% for the respective incorporation rates, with warmer regions such as the Sichuan Basin experiencing the most pronounced emissions due to higher soil pH and temperatures. Regional analysis suggests that full incorporation is most appropriate for northern regions where yield and SOC benefits outweigh GHG increases, while two-thirds incorporation is optimal for southern regions to balance productivity and emissions. In areas such as Yunnan and Jiangsu, where excessive straw has had a negative impact on yield, one-third incorporation is recommended. The study highlights the importance of region-specific strategies, such as off-season straw application or composting, to enhance carbon sequestration and reduce emissions, thereby supporting climate-smart agriculture in China.
Graphical Abstract