May 1, 2024 | Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment | Source |
Introduction: Rice cultivation in Punjab, India, has increased by 56% over the last three decades, severely depleting groundwater reserves (97% of which is used for paddy) and contributing significantly to CHâ‚„ emissions and carbon footprint. Improving water productivity through efficient irrigation management and addressing variability in GHG emissions across rice varieties is therefore essential. Despite the critical role of irrigation and cultivar choice, little research has assessed the trade-off between CHâ‚„ and Nâ‚‚O emissions or the global warming potential (GWP) of long- and short-duration rice cultivars under different irrigation regimes. To address this gap, soil scientists from Punjab Agricultural University conducted a two-year field experiment (2019-2020) to study the effects of rice cultivar duration (long vs. short) and irrigation methods (continuous flooding, CF; irrigation two days after infiltration, 2DAIPW; and three days after infiltration, 3DAIPW) on water productivity, yield, net GHG emissions, and greenhouse gas intensity (GHGI).
Key findings: Crop management, in particular irrigation scheduling and rice variety selection, has a significant impact on crop productivity and GHG emissions. Irrigation affects CHâ‚„ emissions through soil-atmosphere gas exchange, while rice plants affect CHâ‚„ dynamics by providing root exudates for methanogens, enabling CHâ‚„ exchange via aerenchyma, and promoting CHâ‚„ oxidation through oxygen transport. Emissions also vary between cultivars based on characteristics such as growth duration, tillering density and biomass.
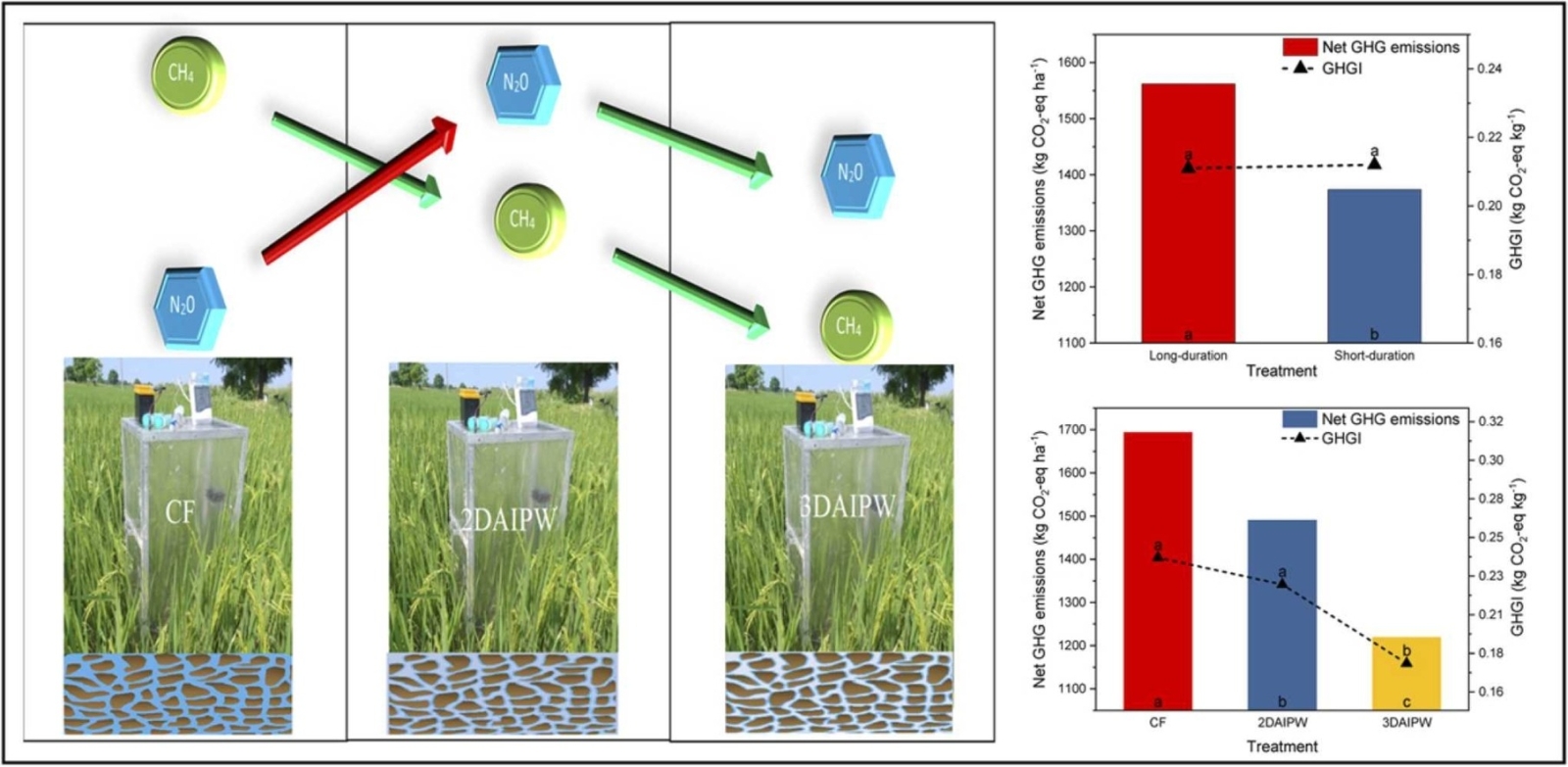
This study found that short-duration rice cultivars reduced water use by 17% and CHâ‚„ and Nâ‚‚O emissions by 12% and 11%, respectively, compared to long-duration cultivars, despite yielding 12% less grain. Among the irrigation regimes, applying water three days after infiltration (3DAIPW) reduced irrigation water use by 31% and CHâ‚„ emissions by 39% compared to CF, although it increased Nâ‚‚O emissions by 29%. In addition, 3DAIPW improved water productivity and reduced GHGI by 26% without significantly affecting yield. The results suggest that combining short-duration varieties with irrigation three days after infiltration can improve resource efficiency and mitigate climate impacts in rice systems. However, the study highlights the need to optimize transplanting schedules for short-duration varieties to maximize their yield potential.
Graphical Abstract