May 5, 2022 | JGR Biogeosciences | Source |
Introduction: Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD), a technique that involves intermittently drying fields to maintain a shallow soil water table, has emerged as a promising irrigation method for reducing CHâ‚„ emissions and water use while sustaining crop yields under optimal management. However, its impact on nitrogen oxide (Nâ‚‚O) emissions remains uncertain. This study, conducted by researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany, uses the process-based biogeochemical model LandscapeDNDC to evaluate AWD's mitigation potential at a national scale in the Philippines over a 12-year period. By analyzing intra- and inter-annual GHG emissions under AWD and CF practices, including off-season patterns, the research aims to advance Tier 3 national GHG inventory methodologies and inform data-driven decisions for scaling AWD adoption as a climate-smart agricultural strategy.
Key findings: This study tested the LandscapeDNDC model using data from 93 cropping seasons in the Philippines to predict GHG emissions and crop growth under various management practices. It incorporated climate, soil, and land-use data to simulate six scenarios, including conventional flooding (CF), rainfed (RF), and Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD). Model accuracy was evaluated using statistical measures, while simulations assessed GHG emission reductions and residue management impacts.
The results revealed that implementing AWD at a national level could reduce methane emissions from irrigated rice fields by approximately 23%, though Nâ‚‚O emissions increased by 15%. Despite this, CHâ‚„ remains the dominant contributor to the global warming potential (>95%) of rice production, both under CF and AWD management. The mitigation benefits of AWD were more pronounced in the dry season (38% reduction in CHâ‚„) compared to the wet season (19%), highlighting the role of weather conditions. Key factors influencing emission reductions included irrigation intensity, residue management, and soil texture. Residue incorporation significantly affected emissions, amplifying CHâ‚„ under all scenarios. Seasonal and spatial factors, including soil texture and water management, played critical roles in determining emission variability. Importantly, the study emphasized the need for consistent and site-specific management to maximize AWD's environmental benefits while mitigating risks, such as yield reductions due to improper water management.
These findings underline AWD's potential as a viable strategy under moderate fertilizer use for reducing GHG emissions in rice cultivation without compromising productivity. Future research should address the variability in Nâ‚‚O emissions and the broader implications of integrating AWD into national GHG inventories. Further refinement of models to capture aerobic processes and irrigation variability is necessary for accurate GHG inventory development and policymaking.
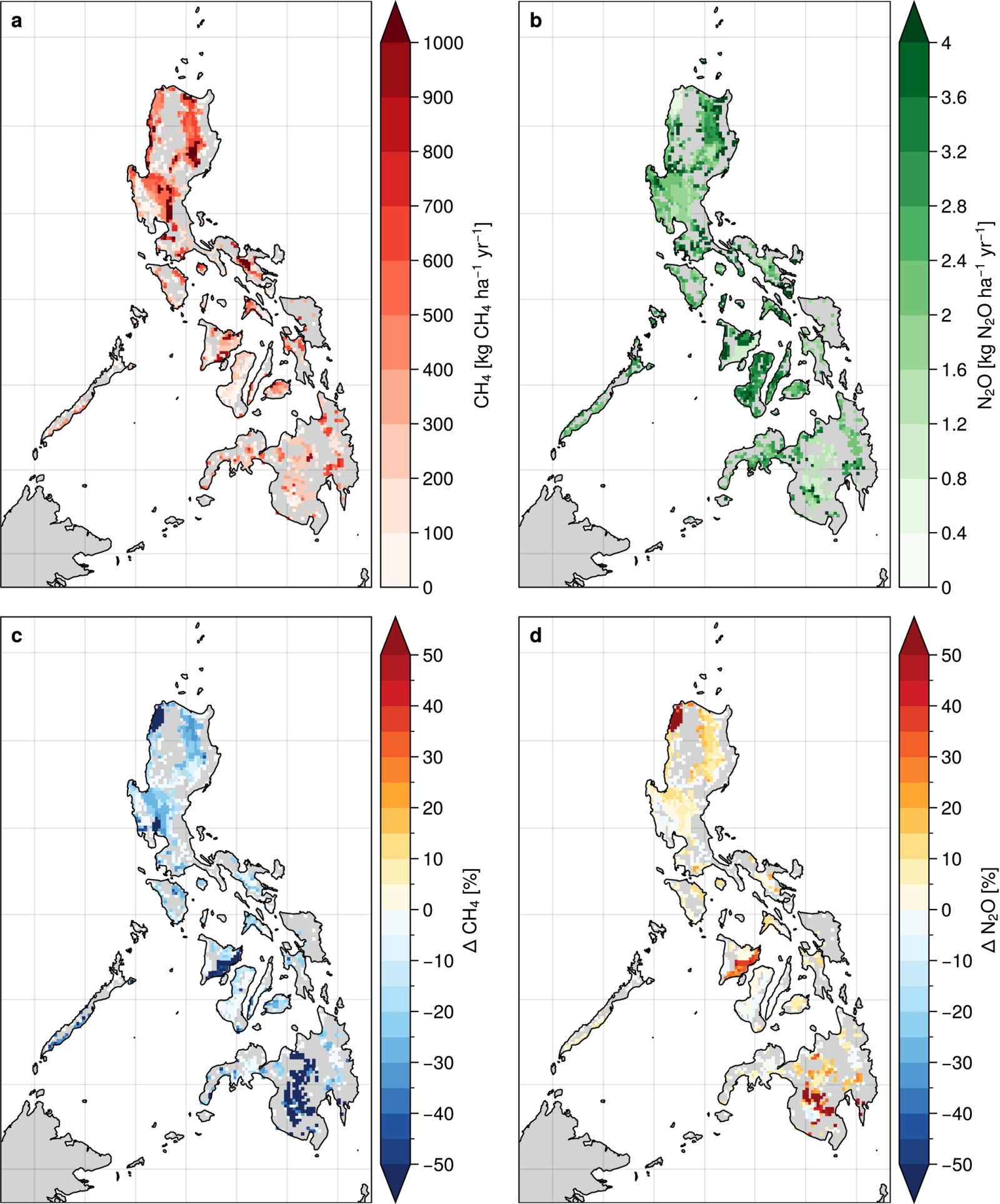
Figure | Panels (a and b) Simulated mean annual (12-year simulation period) emissions of CH4 and N2O for the aggregated CF* inventory corresponding to conventional field management. Panels (c and d) Relative change of CH4 and N2.





