April 17, 2023 | Nature Food
Introduction: The global food system faces challenges from the pandemic, conflicts, resource depletion, biodiversity loss, and climate change. Balancing the need for food with sustainability requires a transformative approach. The concept of a circular food system, minimizing and recycling waste, emerges as a potential solution. Research team from Wageningen University in Netherlands collaborated with researchers from Cyrus and Switzerland to explore redesigning the European food system based on circularity principles, offering insights into consumption, crop and animal production, and fertilizer use for a more sustainable future.
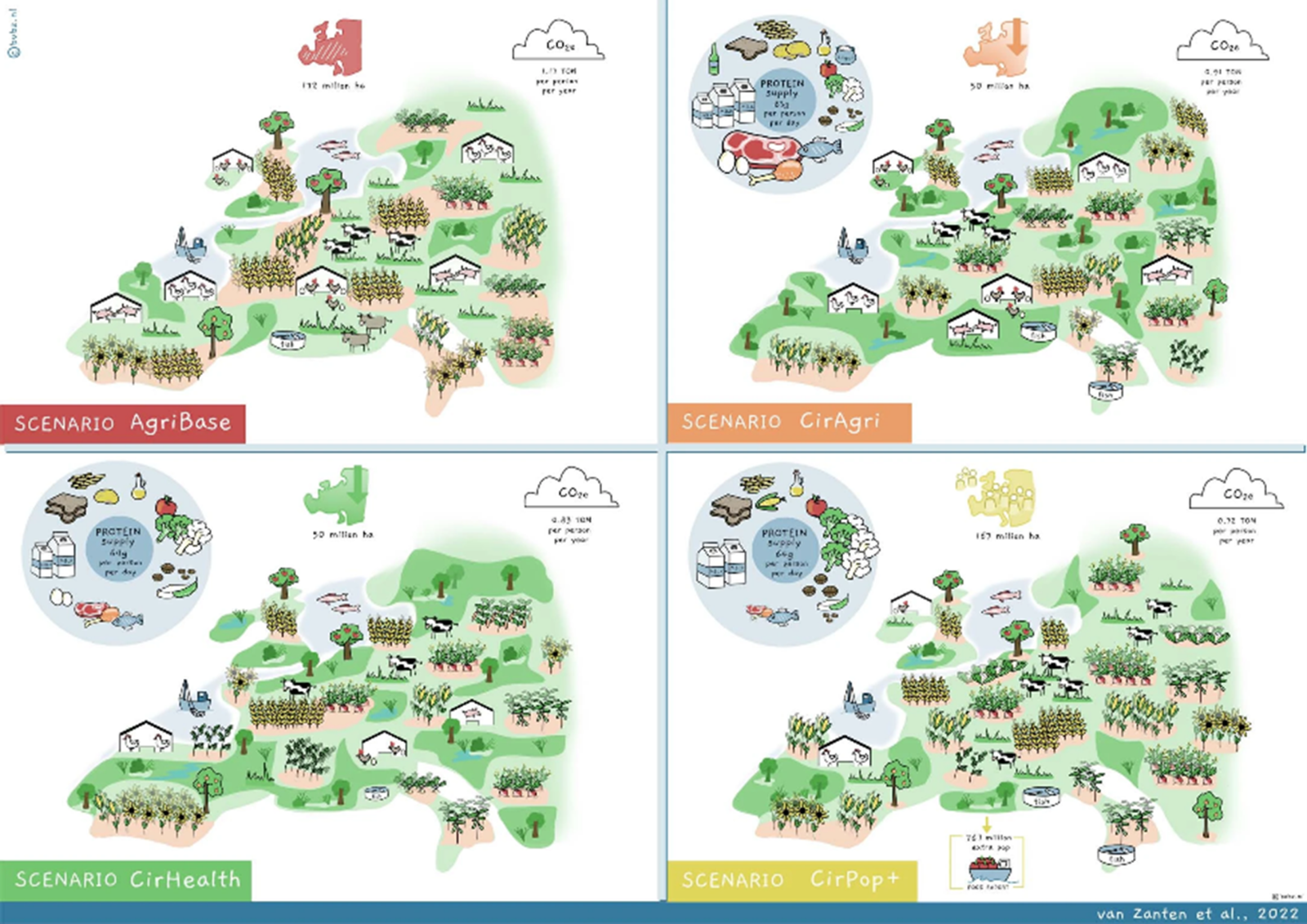
Key findings: By transitioning to a circular food system in the European Union, potential benefits include a 71% reduction in agricultural land use and a 29% decrease in per capita agricultural greenhouse gas emissions. This shift could enable self-sufficiency in producing healthy food. Moreover, amid global food shortages, the saved agricultural land could feed an additional 767 million people outside the EU (a 149% increase) while reducing per capita greenhouse gas emissions by 38%. However, overall emissions would rise by 55% due to the increased population served. This study highlights the transformative potential of circularity in preserving both human and planetary health.
Read more: Circularity in Europe strengthens the sustainability of the global food system
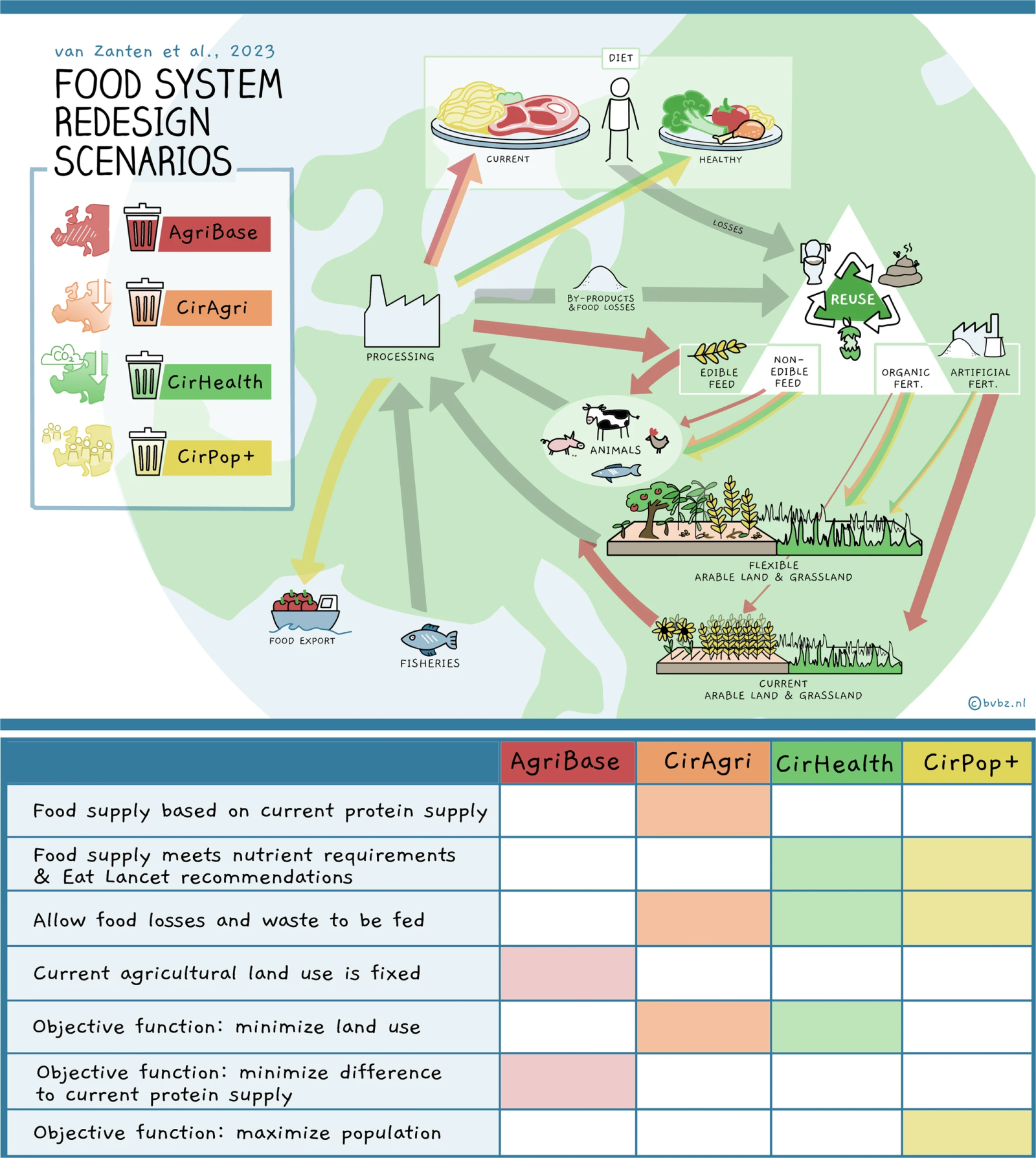
Fig. 1: Scenario configuration and illustration.
The colours of the arrows and icons on the top left represent the different scenarios in the table. The arrows represent uses of biomass that differ among scenarios. In the case of the grey arrows, the assumptions related to the use of biomass are the same for all scenarios.
Extended Data Fig. 1: Visual abstract.