June 29, 2023 | Nature Sustainability |
Introduction: Livestock production, while crucial for economic growth, employment, and nutrition, also poses challenges related to climate change. A transition towards more sustainable and climate-resilient livestock systems is imperative, with the potential to positively impact the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals. A research team from Wageningen University & Research in Netherlands collaborated with researchers from Kenya, France, and Colombia, investigates the exposure of livestock production and rural populations to climate hazards and the associated greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across 132 countrie
Key Findings: Results reveal that significant livestock production value, population, and pasture areas are exposed to climate hazards, with India, Nigeria, and Sudan being the most vulnerable. GHG emissions from livestock are substantial, with Brazil and India contributing significantly. The analysis prioritizes adaptation and mitigation strategies, highlighting India, Brazil, China, Pakistan, and Sudan as crucial focal points due to their combined impact on value of production, population, and emissions. The study emphasizes the need for coordinated efforts in addressing climate risks and adopting mitigation strategies, recognizing the interconnectedness of adaptation and mitigation priorities. The paper underscores existing challenges, including low adoption rates, cost barriers, and regional variations, and advocates for context-specific approaches to ensure effective implementation of climate actions in the livestock sector.
Read more: Priority areas for investment in more sustainable and climate-resilient livestock systems
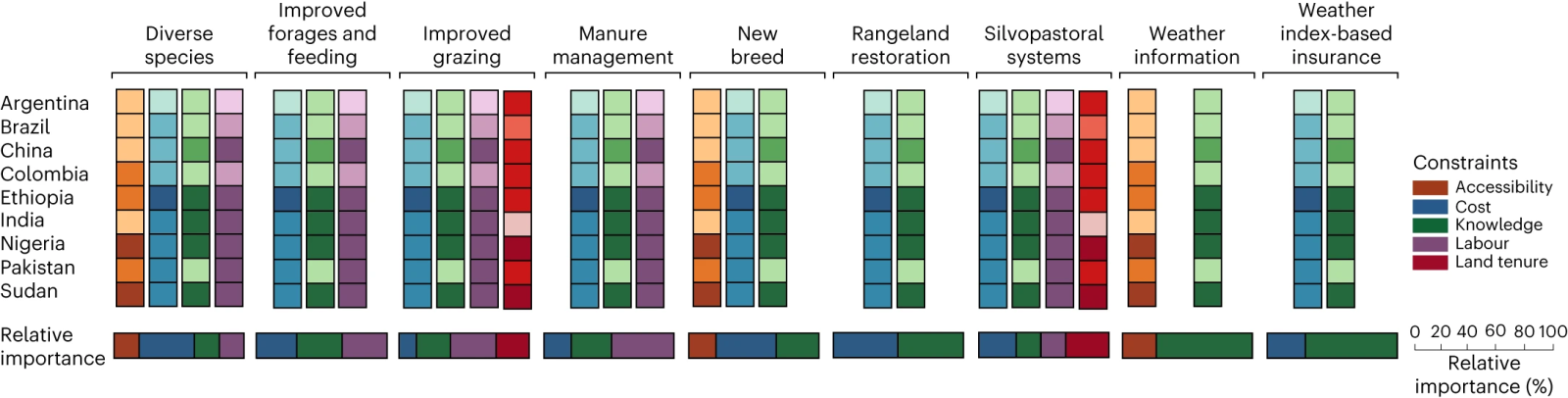
Fig. 3: Adaptation and mitigation options available for livestock systems in LMICs, constraints to their adoption in the selected countries and the relative importance of each constraint for the adoption of each option in general.
Darker colours represent a higher constraint for the adoption of a particular option in each country, as determined by the quantile in which the country sits with respect to the global median. Indicators to represent each constraint include accessibility (research and development expenditure (percentage of GDP)), cost (GDP per capita), knowledge (literacy rate in the total adult population), labour (employment in agriculture) and land tenure (Rule of Law).





