June 5, 2023 | International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment | Source |
Introduction: The study, led by researchers from the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), investigates innovative tools for assessing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and carbon footprints (C-footprints) in rice production. It introduces a digital information system tailored for tracking and labeling rice C-footprints and evaluates mitigation strategies using context-specific GHG metrics. Addressing rice's significant contribution to agricultural emissions (13–14%), the research supports efforts to align rice production with climate goals.
Key findings: The study presents a framework featuring three tools to assess C-footprints and GHG emissions in rice production. The application “DISPLAY” enhances transparency with QR-coded labels, allowing users to customize emission factors based on local practices and technologies. “CF-Rice” monitors emissions along the value chain, enabling detailed tracking of GHG outputs at different stages, while “SECTOR” evaluates mitigation strategies under various scenarios. Key findings reveal that harvest losses contribute 22% of emissions, higher yields reduce C-footprints but increase fertilizer-related emissions, and mitigation strategies, such as multiple drainage systems, reduce methane emissions. Site-specific nutrient management improves nitrogen efficiency by 30–40%, reduces fertilizer use by 25% without yield loss, and significantly decreases nitrous oxide emissions. Together, these tools advance sustainable rice production with the potential for broader applications, particularly in crops like wheat or maize. Their effectiveness depends on high-quality localized data and coordinated stakeholder collaboration to address challenges in scalability and regional adaptability.
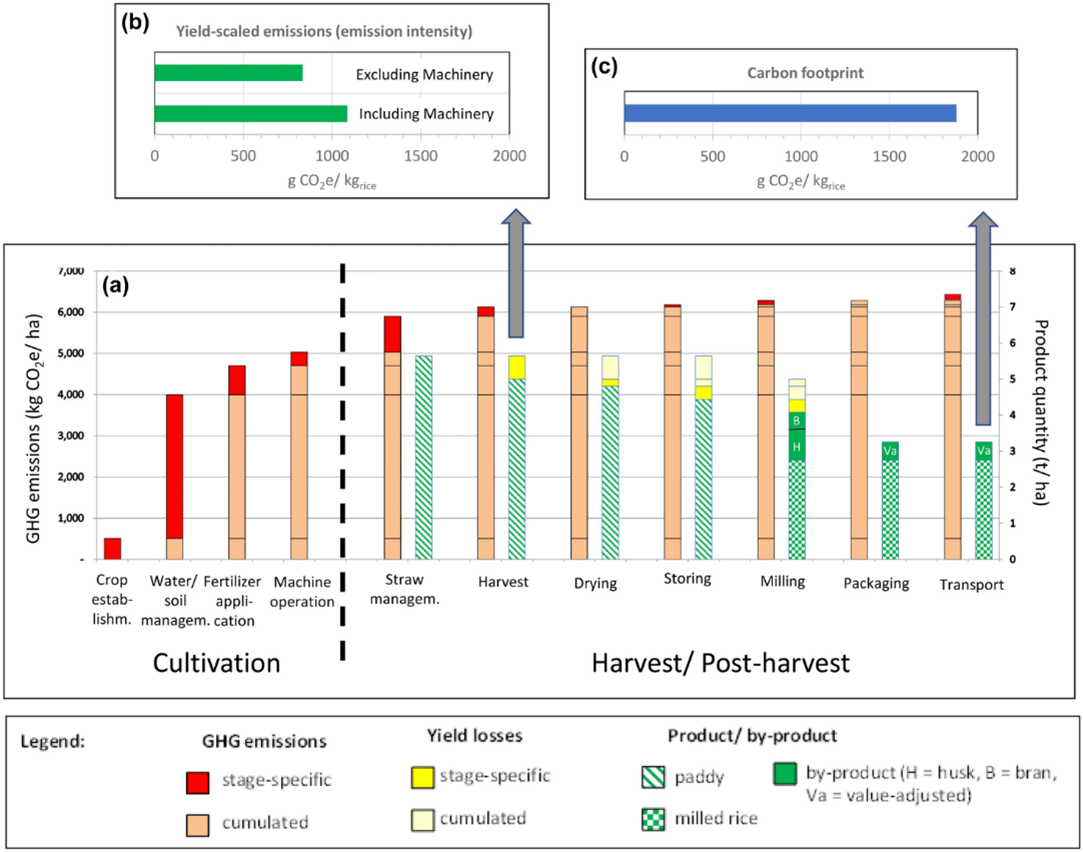
Figure | Accumulation of GHG emissions and product mass balance along the value chain under baseline conditions (a) alongside the yield-scaled emission (b) and carbon footprint (c); arrows indicate the respective stages when these parameters are calculated.





