June 6, 2024 | Science | Source |
Introduction: Methane (CHâ‚„) and nitrous oxide (Nâ‚‚O), greenhouse gases (GHGs) far more potent than COâ‚‚, are emitted via microbial activity in diverse ecosystems. Biologists from the University of Alberta (Canada) and the University of Washington (USA) investigate the trade-offs and unintended consequences of CHâ‚„-Nâ‚‚O mitigation strategies, emphasizing their complex interplay and the need for integrated approaches.
Key findings: Methanotrophs interact with nitrogen cycles, sometimes increasing Nâ‚‚O emissions in low-oxygen environments, while nitrification inhibitors can suppress methanotrophic activity, inadvertently raising CHâ‚„ levels. Promising biology-based CHâ‚„ mitigation methods, such as biofilters and compost biocovers, can reduce CHâ‚„ emissions but may increase Nâ‚‚O levels, underscoring the need for careful monitoring of nitrogen interactions. Critical zones, including rice paddies and landfills, illustrate the complexity of CHâ‚„-Nâ‚‚O trade-offs. Closed bioreactor systems show promise for controlling emissions and producing sustainable bioproducts, though scalability and economic feasibility remain significant challenges. To maximize climate benefits, effective mitigation strategies must integrate comprehensive monitoring, nutrient management, and innovative amendments. Tailored interventions across diverse environmental contexts are crucial for achieving sustainable outcomes globally.
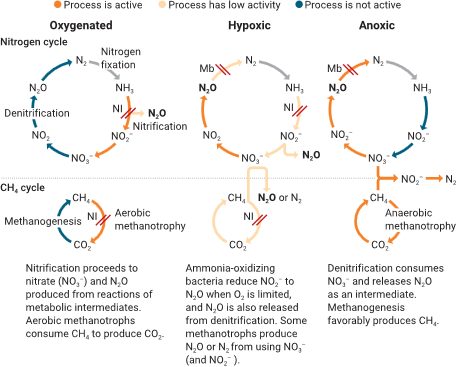
Figure | Microbial processes controlling methane and nitrous oxide production. Nitrification inhibitors (NI) can block both nitrification and aerobic methanotrophy, preventing methane (CH4) consumption and nitrous oxide (N2O) production. Methanobactin (Mb) blocks N2O consumption, potentially increasing N2O emissions.





