January, 2023 | Heliyon | Source |
Introduction: Azolla, an aquatic fern with nitrogen-fixing capabilities through its symbiotic association with Aenabana azollae, has the potential to serve as an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to chemical fertilizers. Despite its benefits on soil fertility, nitrogen use efficiency, reducing weed competition, and mitigating emissions—its adoption remains limited among rice farmers. This study, conducted by researchers from the Ministry of Education and Vocational Training, and Sokoine University of Agriculture in Tanzania, systematically reviews the benefits, constraints, and application strategies of Azolla in lowland rice production using the PRISMA method.
Key findings: The study highlights several key aspects of Azolla's role as a biofertilizer:
- Soil Fertility and Nutrient Cycling: Azolla significantly enhances soil organic matter, increases microbial biomass, and improves soil nutrient availability. Its incorporation into rice fields can replace up to 60 kg N ha‚ĀĽ¹ of synthetic fertilizer.
- Nitrogen Fixation and Release: Anabaena azollae within Azolla fixes atmospheric nitrogen, providing an essential nutrient source for rice. When used as green manure, 56–75% of its nitrogen content becomes available to the rice crop within 3–6 weeks after application.
- Weed Suppression: A dense Azolla mat reduces light penetration, suppressing weed emergence and decreasing reliance on herbicides.
- Reduction of Ammonia Volatilization: Azolla lowers floodwater pH and temperature, thereby reducing nitrogen loss due to ammonia volatilization.
- Enhanced Rice Yield: Studies indicate that incorporating Azolla into rice fields can increase grain yield by 27–36%, comparable to full nitrogen fertilization.
- Constraints to Adoption: Despite its benefits, Azolla cultivation faces several challenges, including high labor requirements for incorporation, the need for phosphorus supplementation, and the difficulty of maintaining consistent biomass production across different agroecological zones.
To enhance the adoption of Azolla as a biofertilizer, strategic initiatives should focus on farmer education, research into species-specific performance, development of cost-effective application methods, and policy support for integrated nutrient management. Expanding its use in sustainable rice production could significantly contribute to improving soil health, reducing dependency on synthetic fertilizers, and promoting climate-smart agricultural practices.
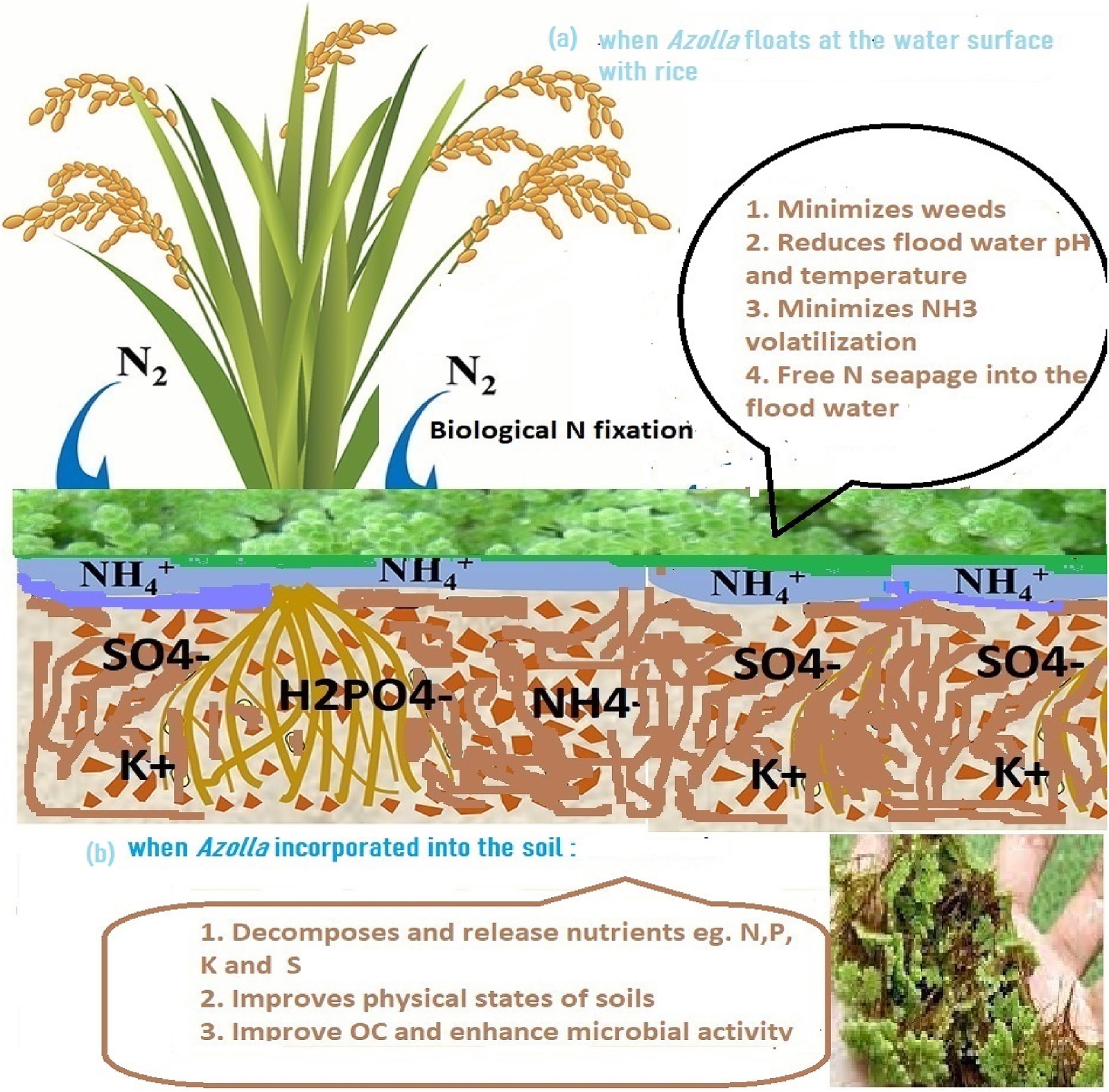 Figure | Illustration showing some benefits of Azolla biofertilizer when either left flooded (a) or incorporated in the soil (b).
Figure | Illustration showing some benefits of Azolla biofertilizer when either left flooded (a) or incorporated in the soil (b).










