March 19, 2024 | Environmental Science & Technology | Source |
Introduction: This study, conducted by researchers from Hunan University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, evaluates the historical carbon footprint (CF) of rice production across China’s counties from 2007 to 2018. By integrating Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) with the Denitrification-Decomposition (DNDC) model, the study quantifies spatial and temporal variations in CF and identifies key driving factors and mitigation strategies.
Key findings: The farm-based carbon footprint (FCF) of rice production increased by 74.3 kg CO‚āā-eq ha‚ĀĽ¹ per year between 2007 and 2018, while the product-based carbon footprint (PCF) remained stable. CH‚āĄ emissions from paddy fields were the dominant contributor to FCF, followed by diesel consumption and soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration. Spatial analysis revealed significant regional disparities, with high FCF concentrated in the North China Plain and the Middle-Lower Yangtze Plain.
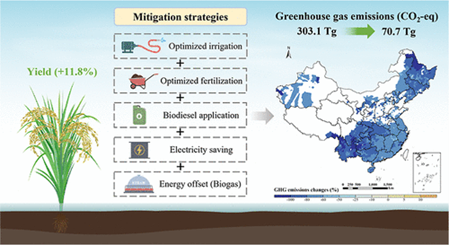
Scenario analysis showed that optimized irrigation, particularly alternate wetting and drying (AWD), could reduce national GHG emissions from rice production by 48.5%, while utilizing rice straw for biogas production could cut emissions by 18.0%. Combining multiple mitigation strategies—including improved crop management, optimized fertilization, and biodiesel use—could achieve a 76.7% reduction in emissions while increasing rice yield by 11.8%. The study underscores the need for targeted policies to implement AWD irrigation, optimize nitrogen fertilizer use, and promote bioenergy utilization to advance China’s low-carbon agriculture goals.