April 27, 2021 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | Source |
Introduction: This review, led by scientists from the Department of Environmental Sciences at Central University of Jharkhand in India, examines the methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from rice fields in India. It analyzes data from various locations to assess the impacts of field and crop management practices, highlighting the need for precise quantification to inform effective mitigation strategies.
Key findings: Research indicates that the highest CHâ‚„ emissions occur under continuously flooded conditions, while intermittently flooded rice fields produce less CHâ‚„ but more Nâ‚‚O. The primary strategies for reducing emissions in Indian rice fields covered include:
- Irrigation Management – Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) can cut CHâ‚„ emissions by 22-75% compared to continuous flooding.
- Tillage Practices – Zero and reduced tillage methods help lower CHâ‚„ emissions by reducing soil organic matter decomposition.
- Fertilizer Management – Applying slow-release fertilizers, nitrification inhibitors (e.g., dicyandiamide), and organic amendments like biochar reduces both CHâ‚„ and Nâ‚‚O emissions.
- Rice Cultivar Selection – Certain cultivars with lower aerenchyma transport CHâ‚„ and Nâ‚‚O less efficiently, making them more sustainable options.
- Manure Management – Incorporating green manure and compost instead of synthetic fertilizers can significantly reduce GHG emissions.
The review highlights the urgent need for integrated mitigation strategies tailored to India's diverse rice ecosystems. Adoption of improved water, soil, and fertilizer management techniques can help balance high rice productivity with environmental sustainability while aligning with India's climate commitments.
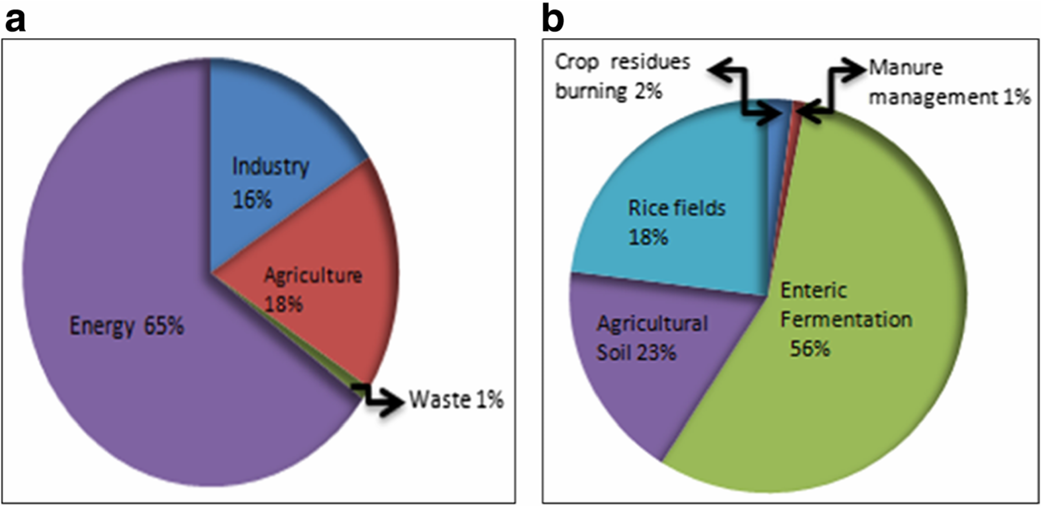
Figure | Emanation of greenhouse gas from a. different sector from Indian economy and b. sub sectors of agriculture in 2010





