November 11, 2024 | Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology | Source |
Introduction: Addressing the growing threat of soil degradation, researchers from the University of Prince Edward Island in Canada and Jiangsu University in China conducted a critical review of over 100 studies on biochar—a carbon-rich material from pyrolyzed biomass—providing an integrated analysis of biochar’s effects on soil health, crop productivity, GHG mitigation, and economic viability.
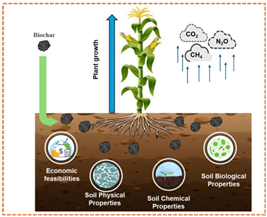
Key findings: Biochar improves soil physical properties by enhancing soil porosity (SP) and reducing bulk density (BD), leading to better water infiltration and retention, and making soil more resilient. Chemically, it raises pH in acidic soils, boosts cation exchange capacity (CEC) and organic carbon levels, and improves nutrient availability while reducing leaching and immobilizing heavy metals. Biologically, biochar fosters microbial growth and activity by providing a supportive habitat, though effects vary with soil type and biochar characteristics.
Incorporating biochar into soil can boost crop yields by 10-16% by enhancing soil properties and nutrient availability. However, results vary with soil type, crop species, and biochar characteristics. Biochar also mitigates GHG emissions by stabilizing soil carbon, reducing Nâ‚‚O through effects on nitrification and denitrification, and lowering CHâ‚„—especially in flooded soils—by enhancing microbial processes and enabling slow-release fertilization. Economic feasibility depends on whether yield gains and input savings outweigh the costs of production, transport, and application, which vary by region and crop. Carbon market incentives can further enhance viability.
Key research gaps include optimizing biochar for specific soils, conducting long-term field studies, and assessing large-scale environmental impacts. Future work should prioritize cost–benefit analyses, farmer guidance, and meta-analyses to support broader, sustainable adoption.
Graphical abstract