June, 2024 | Trends in Microbiology | Source |
Introduction: Excessive nitrification in agroecosystems causes nitrate leaching and Nâ‚‚O emissions. Although nitrification inhibitors (NIs) reduce nitrogen losses, their efficacy varies due to interactions among soil conditions and microbial communities. A Belgian-Spanish team led by Ghent University and Universidad del País Vasco reviews the microbiology of nitrification, NI mechanisms, aiming to understand how microbial and abiotic factors influence NI performance. The goal is to inform the development of more targeted, efficient NIs for sustainable nitrogen management.
Key findings: Nitrification in agroecosystems is primarily driven by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), archaea (AOA), and comammox bacteria, which catalyze the rate-limiting step of ammonia oxidation. Their responses to NIs vary, depending on microbial traits and environmental conditions. Common NIs like DCD, DMPP, and nitrapyrin mainly target AOB, while few—such as PTIO and SIAS—affect AOA. No specific inhibitors currently exist for heterotrophic nitrifiers. The study highlights that soil pH, organic matter, clay and copper content, nitrogen levels, and temperature strongly shape the composition of the nitrifying community and thus influence NI effectiveness. For instance, acidic soils favor AOA, weakening AOB-targeted inhibitors, while higher temperature can positively affect AOA abundance and potentially lower the efficiency of DMPP and DCD.
NI application can also shift microbial dynamics, increasing non-target nitrifiers and reducing overall inhibition. Co-application of AOA- and AOB-targeting NIs emerges as a promising strategy. The study identifies key gaps—including NI persistence, microbial resistance, and the contribution of heterotrophic nitrifiers—and calls for broader NI testing, microbiome integration, and further exploration of crop-derived biological NIs. Policy incentives and site-specific NI strategies are crucial to enhance nitrogen use efficiency and reduce emissions in agriculture.
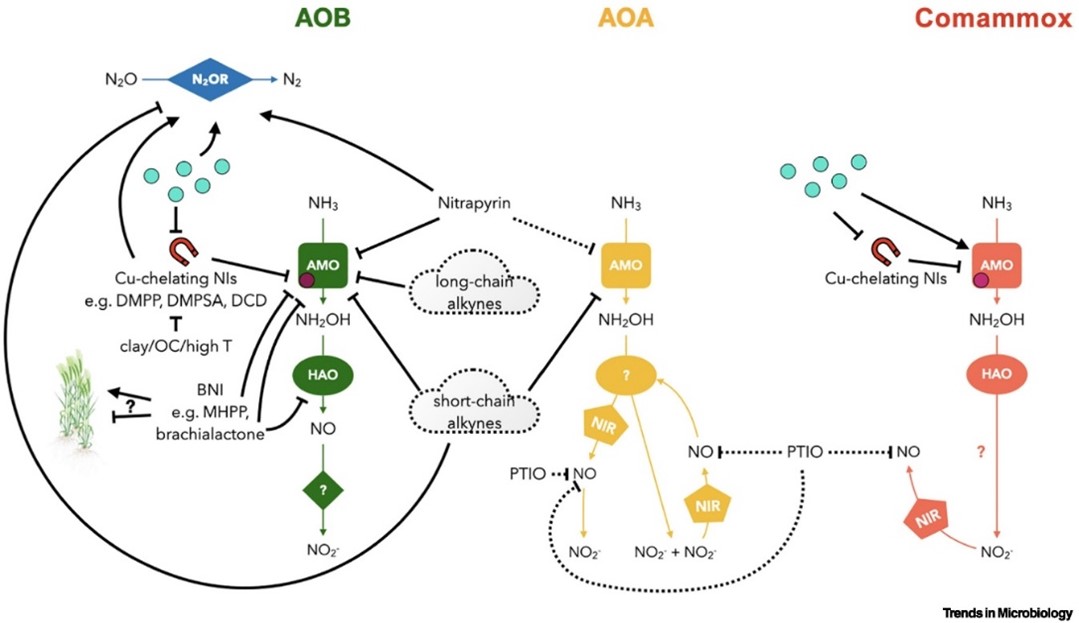
Figure | Targets and effects of NIs in different ammonia-oxidation pathways.





