October 20, 2022 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source |
Introduction:
While organic livestock systems are often hailed as environmentally friendly, their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and carbon sequestration potential vary considerably depending on management practices. This study, led by researchers from Universidad de Extremadura in Spain, investigates how technical-economic factors influence the environmental performance of 34 organic beef cattle farms in the dehesa agroforestry system of southwest Spain.
Key findings:
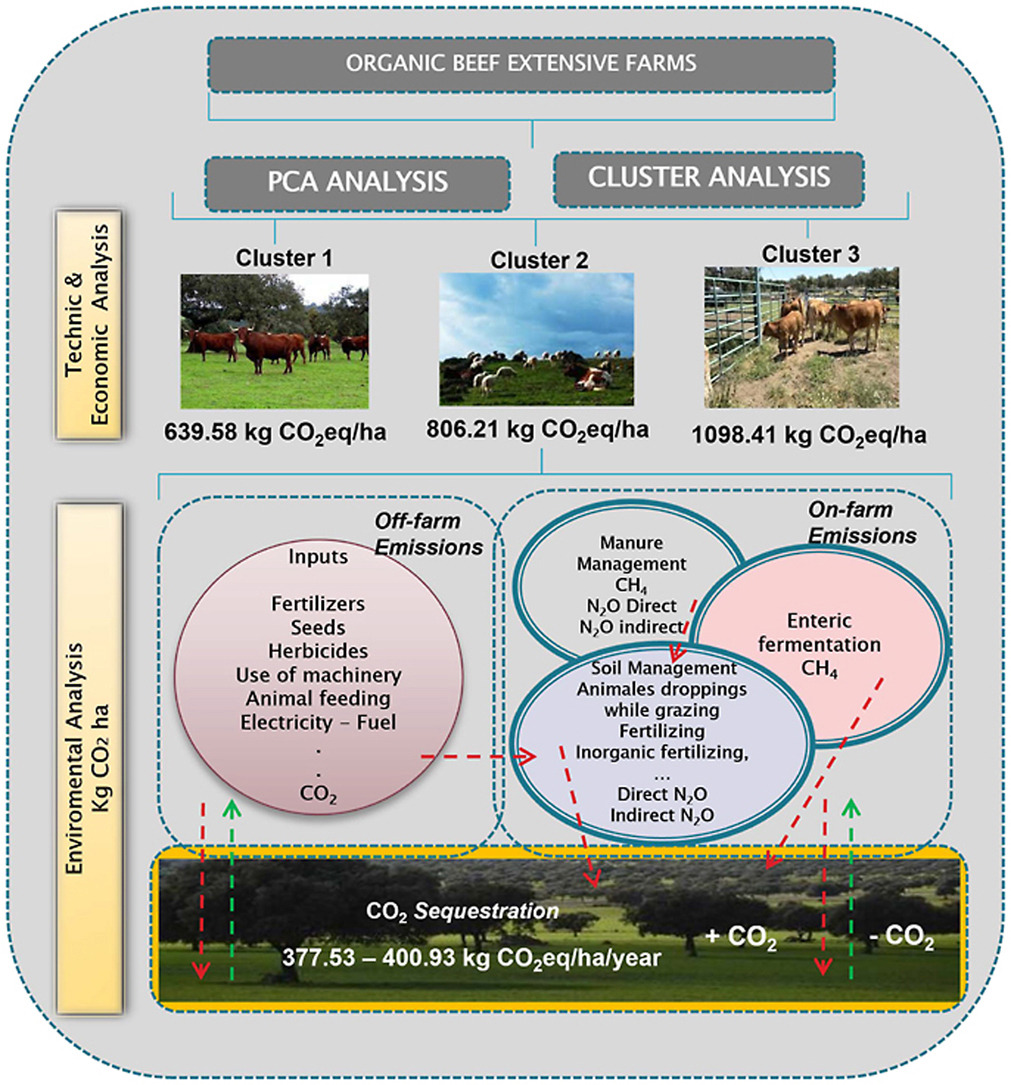
Using principal component and cluster analysis, the study categorizes farms into management types based on factors such as subsidy dependence, production intensity, and feeding practices. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is then used to evaluate farm-level GHG emissions and carbon sequestration. Farms were grouped into three clusters: (1) large, extensive cattle-only farms with low inputs and low subsidy reliance; (2) mixed livestock farms with moderate intensification and crop integration; and (3) small, highly intensive operations with high production costs and diverse species.
Net GHG emissions varied significantly: cluster 1 farms had the lowest net emissions (262.05 kg COâ‚‚e/ha or 6.02 kg COâ‚‚e/kg of live weight sold), while cluster 3 recorded the highest (697.49 kg COâ‚‚e/ha or 11.18 kg COâ‚‚e/kg). The study highlights the significant carbon sequestration capacity of dehesa systems—averaging 386.1 kg COâ‚‚e/ha/year—due to permanent grasslands, manure deposition, and crop residues. Less intensive farms benefited most from this sequestration, offsetting a larger portion of their emissions. These findings underscore the importance of tailored farm management strategies—such as controlled stocking rates and improved grazing practices—to enhance carbon efficiency. The study calls for standardizing how carbon sequestration is integrated into environmental assessments and advocates for policies that support extensive systems as climate-resilient, multifunctional land uses.
Graphical abstract