January 15, 2022 | Atmosphere | Source |
Introduction:
Livestock both drives and suffers from climate change, contributing 14.5% of global GHG emissions while facing growing climate-induced stress. Researchers from Texas A&M University reviewed 157 studies to examine climate impacts, emission sources, and feasible adaptation and mitigation strategies for more resilient and sustainable livestock systems.
Key findings:
- Climate Impacts on Livestock Production: Climate change affects livestock through direct and indirect pathways, driven by rising temperatures, variable precipitation, and more frequent extreme events. Direct impacts include reduced feed intake, lower milk, meat, and egg production, impaired fertility, weakened immunity, and increased mortality—primarily due to heat stress. Indirectly, climate change degrades forage quality, limits water availability, and increases exposure to pests and diseases, reducing overall productivity and system resilience.
- Impact of Livestock Production on Emissions: Emissions arise directly from animal processes and indirectly from feed production and land-use change. CHâ‚„ from enteric fermentation and Nâ‚‚O from manure dominate direct emissions. Indirect emissions stem from feed production, processing, transport, land-use change for pasture and feed crops, and energy use across the supply chain. Cattle are the largest contributors, accounting for about 62% of sectoral emissions, with variation by species, systems, and regions.
- Adaptation: Adaptation includes both animal responses and human interventions. Livestock adapt through behavioral, physiological, biochemical, immunological, and anatomical changes, though high-yielding breeds are particularly vulnerable to heat stress. Human strategies include breeding heat-tolerant species, enhancing housing and ventilation, adjusting feed and water practices, and adopting integrated crop–livestock systems suited to local contexts.
- Mitigation: Emissions can be reduced through strategies targeting specific gases. Feed additives and dietary changes reduce CHâ‚„; anaerobic digestion and improved manure management lower CHâ‚„ and Nâ‚‚O; and precision fertilizer use and land management mitigate Nâ‚‚O and COâ‚‚. These measures could cut sectoral emissions by up to 30%. Yet, locally tailored solutions are essential, especially in developing regions where resources are limited.
The review identifies key research gaps, including limited focus on non-ruminant species, underexplored mixed crop–livestock systems, and a lack of context-specific strategies. It calls for expanded research and policy support to scale effective solutions, particularly in vulnerable regions.
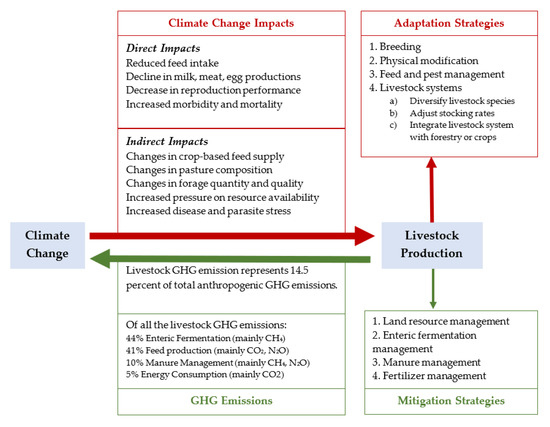
Figure | An overview of the relationship between climate change and livestock production.





