March 13, 2022 | Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture | Source |
Introduction: Food loss and waste are major environmental concerns, contributing to 29% of global GHG emissions, with especially high levels at the consumer stage. To address this, researchers from the University of Beira Interior and Center for Mechanical and Aerospace Science and Technologies (C-MAST) in Portugal conducted a PRISMA-based review of 108 studies on smart packaging across agro-industrial sectors. While meat and general topics dominated the literature, the review identified notable research gaps in dairy, fruits and vegetables, and particularly bakery and pastry—sectors needing targeted innovation due to unique commercial or technical constraints.
Key findings: Unlike active packaging, which directly interacts with food to extend its shelf life, smart packaging focuses on monitoring and communicating product conditions without altering the product itself. The study identified Time Temperature Indicators (TTIs), freshness indicators (monitoring microbial metabolites), gas indicators, sensors (physical, chemical, and biosensors), and data carriers (QR codes and RFID tags) as effective smart packaging technologies. TTIs were found to be especially cost-effective and broadly applicable, offering a clear indication of temperature history and food quality. Meanwhile, QR codes and RFID tags demonstrated strong potential for enhancing traceability, preventing fraud, optimizing logistics, and engaging consumers through features like augmented reality.
The review identified challenges such as sensor affordability, complex RFID integration, and the need for progress in printed electronics and biosensor miniaturization. It highlighted the value of synergistic technologies—like RFID with humidity, pH, and temperature sensors—for more effective monitoring. Chipless RFID emerged as a promising, low-cost alternative, though further advances in materials and printing are needed. Future research should address these gaps to improve the scalability and effectiveness of smart packaging for sustainable agrifood systems.
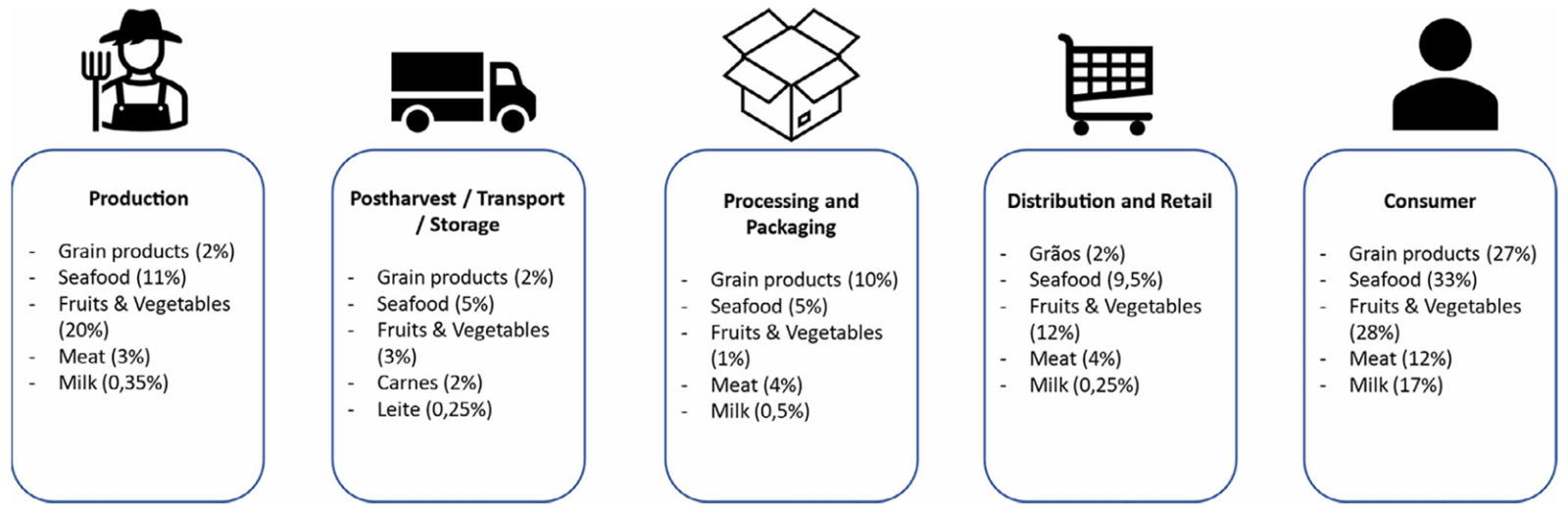
Figure | Food loss and waste in various stages of the food supply chain. Adapted from Chen et al.





