June 24, 2024 | Humanities and Social Sciences Communications |
Introduction: Digital inclusive finance is widely promoted as an enabler of green transitions, yet its environmental impacts in agriculture remain underexplored. A Chinese research team led by the College of Management at Ocean University of China analyze provincial-level data (2011–2021) to examine how digital inclusive finance affects agricultural carbon emissions. By applying fixed-effects and non-linear threshold models, the study investigates whether expanding financial access translates into measurable emission reductions.
Key findings: Using provincial data (2011–2021), the study first documents clear spatiotemporal patterns in China’s agricultural carbon emissions: emissions follow an inverted U-shape, peaking in 2015 before declining; regionally, the east–west gap narrows while the north–south gap widens, implying the need for differentiated regional mitigation strategies. Econometrically, digital inclusive finance (DIF) shows a non-linear (inverted U-shaped) effect on emissions—early-stage DIF expansion is associated with higher emissions, but emissions are suppressed once DIF surpasses the turning point. Importantly, the mitigation effect is driven mainly by usage depth and degree of digitization, rather than coverage breadth, suggesting policy should prioritize effective use and digital capability over simply expanding access.
A key counterintuitive result concerns agricultural green cooperatives: their development weakens DIF’s emission-reduction effect, indicating a “decoupling” rather than synergy—potentially reflecting path dependence and internal management capacity that reduces reliance on external finance, or limits how added finance translates into low-carbon investments. Human capital, by contrast, strengthens DIF’s mitigation effect, reinforcing the value of farmer training and skills in turning finance into measurable decarbonization.
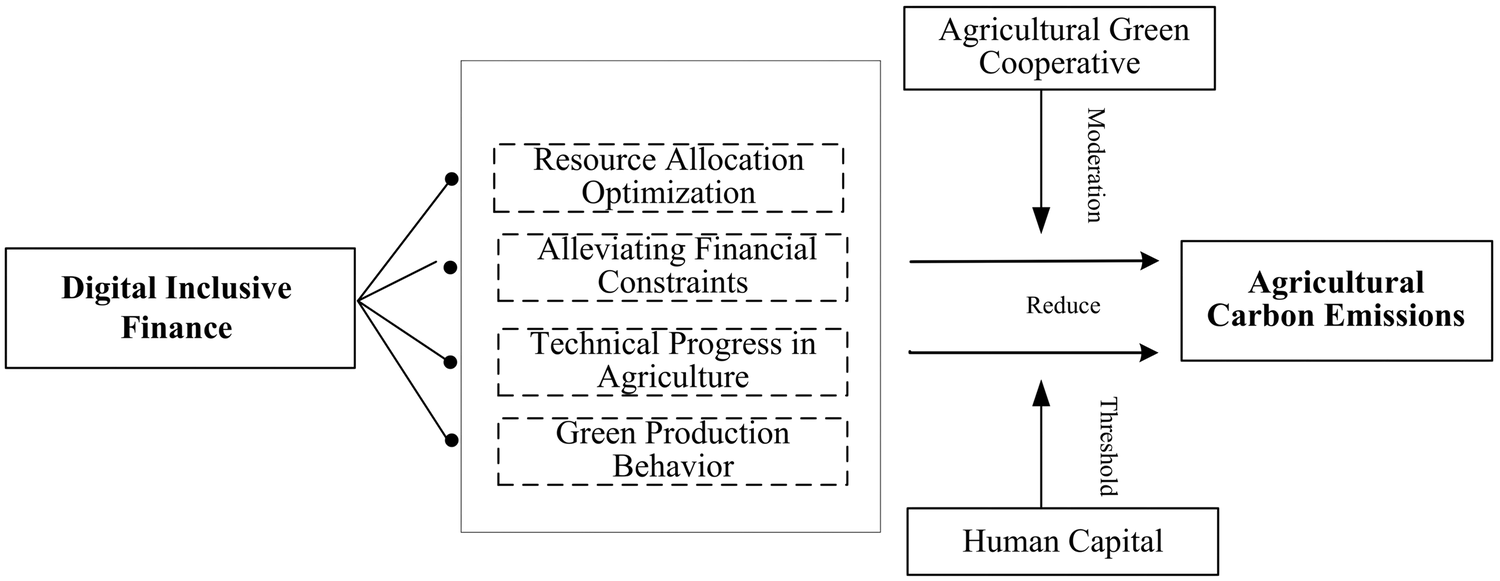
Figure | Mechanism map of the impact of digital financial inclusion on agricultural carbon emissions.





