February 25, 2024 | Journal of Cleaner Production |
Introduction: Place-based agricultural policies are increasingly adopted to balance food security with environmental sustainability, yet their impacts vary widely across regions. A research team from the School of Economics and Trade at Hunan University, China evaluates the effects of China’s agricultural cleaner production place-based policies on agricultural green development (AGD). Using county-level panel data and a difference-in-differences empirical framework, the study assesses how different policy instruments and their combinations influence green development outcomes across diverse regional contexts.
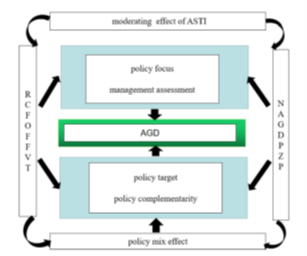
Key findings: The analysis confirms strong policy heterogeneity across China’s agricultural cleaner production place-based policies (ACPBP). The RCFOFFVT program (replacing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers for fruits, vegetables, and teas) is associated with lower AGD, with a stronger inhibitory effect in low-economic-development counties and major grain-producing counties. By contrast, the NAGDPZP (National Agricultural Green Development Pioneer Zone policy) significantly promotes AGD and shows persistence over time, with its positive effects stronger in high-economic-development counties and non-major grain-producing counties—suggesting that implementation capacity, material foundations, and local innovation conditions shape policy effectiveness.
The study also provides actionable insight on policy interactions. In counties with contemporaneous low-carbon policies, the inhibitory effect of RCFOFFVT becomes statistically insignificant (partly offset), while the promotional effect of NAGDPZP becomes weaker, implying that overlapping environmental policies may generate supportive offsets in some cases but also dilute marginal gains when multiple initiatives compete for attention and resources. Finally, policy design matters: policy mixes (RCFOFFVT + NAGDPZP) jointly promote AGD, and agricultural science and technology innovation (ASTI) weakens RCFOFFVT’s negative effects while strengthening NAGDPZP’s positive role, reinforcing the need for capacity-aware, locally tailored policy packages.