March, 2024 | Journal of Agriculture and Food Research |
Introduction: Climate change is undermining agrifood productivity and producer incomes, with small-scale farmers facing heightened exposure due to limited resources and infrastructure. In this review, a research team from the Université Nationale d’Agriculture and the Université d’Abomey-Calavi from Benin synthesizes recent climate-smart innovations that aim to raise producer incomes while safeguarding food security. The paper frames the evidence using the 3 core principles of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) and then links innovations and real-world examples to these objectives, ending with emerging technology directions.
Key findings: The review structures CSA around 3 core principles: sustainable intensification, adaptation, and mitigation, and uses this framework to assess income-enhancing innovations across the agrifood system. Beyond these pillars, the authors emphasize enabling conditions, including social equity, notably gender equality through equal access for women to resources, decision-making, and climate-adaptive practices. Evidence across technologies and practices suggests that precision agriculture, resilient varieties, agroforestry, and regenerative approaches can improve resource-use efficiency, resilience, and profitability, but adoption is constrained by finance, technical capacity, and knowledge gaps. Importantly, the review highlights digital innovations as both near-term enablers and future frontiers. It describes how AI and data analytics can support data-driven decisions from field management to supply-chain efficiency, while blockchain can strengthen traceability and trust, potentially improving access to premium markets. The authors also spotlight emerging directions such as biological computing for intelligent sensing and data storage, and digital twins for proactive scenario planning and resource optimization, while noting that costs, accessibility, expertise, and resistance to change remain central implementation barriers.
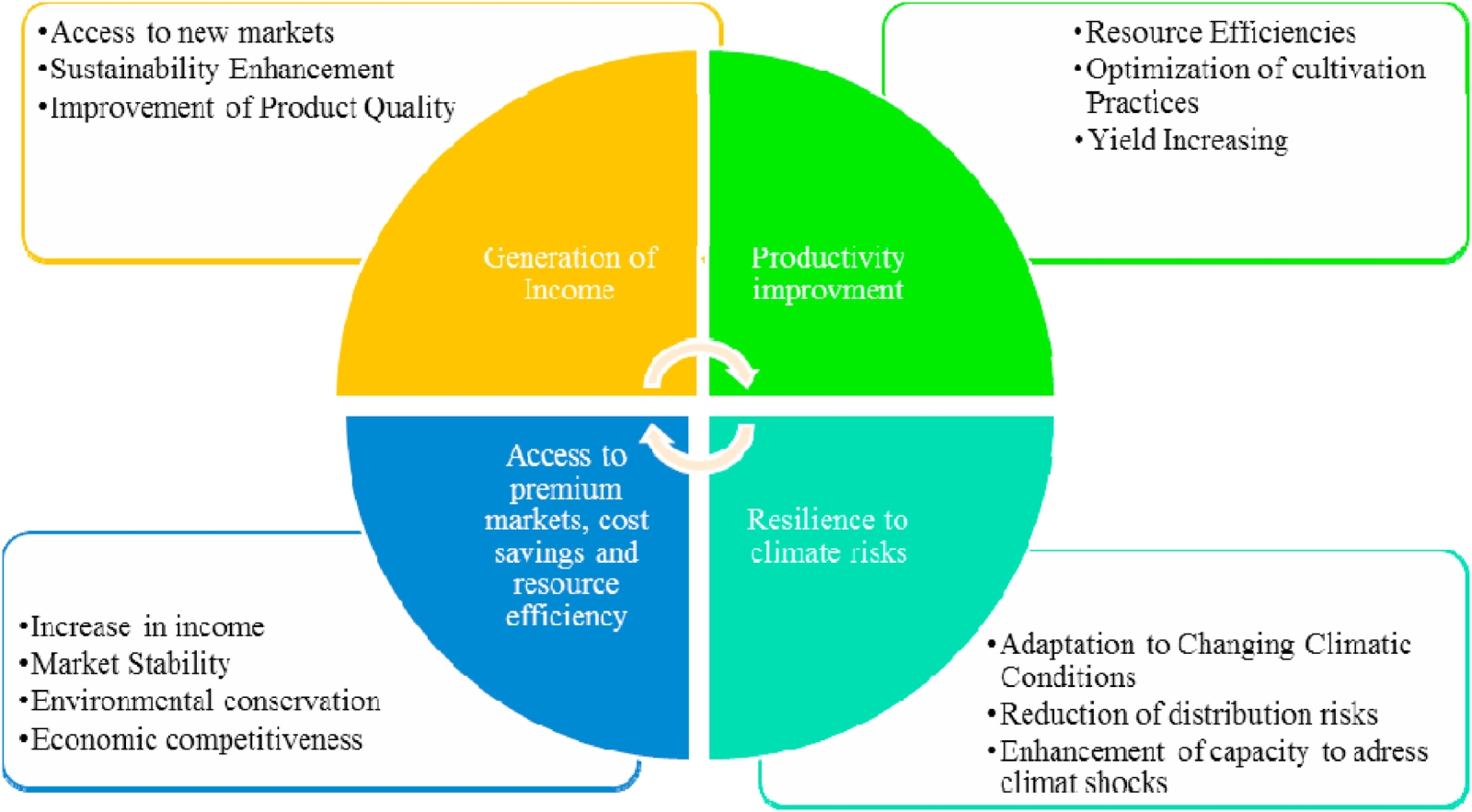 Figure | Climate-smart innovations and their impact on productivity, resilience, income generation, access to premium markets, cost savings, and resource efficiency.
Figure | Climate-smart innovations and their impact on productivity, resilience, income generation, access to premium markets, cost savings, and resource efficiency.





