Divergent effectiveness of irrigation in enhancing food security in droughts under future climates with various emission scenarios
May 23, 2023 | NPJ CLIMATE AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE
In this study conducted by the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hong Kong Baptist University, and other international institutions, researchers aimed to understand the impact of irrigation on food security during droughts under future climate conditions with different emission scenarios. Food security is a crucial goal in the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and China, being the most populous developing country, faces significant challenges in this area.
Using the modified Palmer Drought Severity Index, the team assessed the severity of droughts and analyzed the resulting wheat yield losses in both irrigated and non-irrigated agriculture across China. They employed three methods, including Multiple Linear Regression, Deep Learning algorithms, and the Erosion-Productivity Impact Calculator model. The results indicated that droughts are projected to become more severe in the future, with expected wheat yield losses ranging from 32% to 49% under the high-emission RCP8.5 scenario.
Interestingly, the study revealed that irrigation could effectively reduce drought-induced crop-yield losses under the moderate-emission RCP2.6 and RCP6.0 scenarios. However, in the high-emission scenario, RCP8.5, the effectiveness of irrigation in enhancing food security was found to be limited. These findings underscore the importance of mitigating climate change to ensure future food security and prompt a reassessment of the role of irrigation in a warming climate.
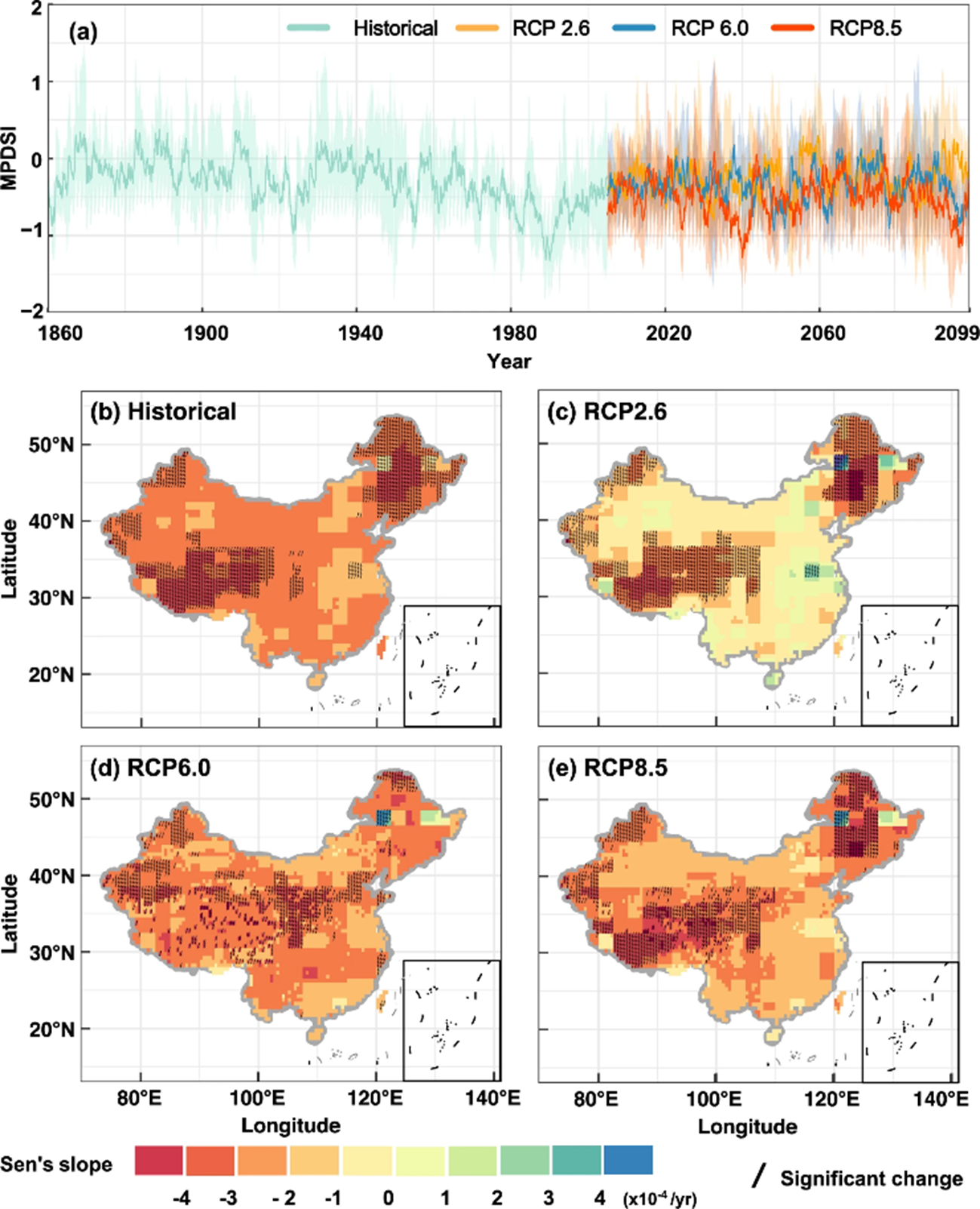
Historical and future changes in modified Palmer Drought Severity Index (MPDSI) in China from 1860 to 2099. An Annual-mean MPDSI based on the multiple ISIMIP datasets under historical (1860–2004) and future scenarios (2005–2099). The future scenarios include the Representative Concentration Pathways 2.6 (RCP2.6), RCP6.0, and RCP8.5. The bold curve is the multi-model mean, and the range shows the maximum and minimum values of the four GCMs. b–e Spatial distribution of the Sen’s slope of MPDSI across China in modified Mann-Kendall (MMK). The diagonal line indicates that the trend is significant at the 99% level.
Viewed Articles
May 23, 2023 | NPJ CLIMATE AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE In this study conducted by the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hong Kong Baptist University, and other international institutions, researc
Read More
July 14, 2025 | Land |  Introduction: Digital and precision agriculture are widely recognized for improving farm efficiency, yet less is known about their broader social and institutional effects on t
August 26, 2023 | Plants | Introduction: A recent collaborative study by National United University, Taiwan, and HCMC University of Technology and Education, Vietnam, addresses the need for efficient
February 28, 2023 | Advances in Applied Energy |  Introduction: Researchers from Cornell University in USA proposed the use of novel artificial intelligence (AI)-based control framework to enhance the
November 07, 2022 | Molecular Plant |  Introduction: Climate change and population growth necessitate a transition from traditional phenotypic selection to data-driven "smart breeding". A research tea
October 16, 2023 | Nature Food |  Introduction: Air pollution and climate change are interconnected challenges that impact field crop production and agroecosystem health. Adapting crop production to t