April 22, 2023 | CLIMATIC CHANGE
Researchers from the Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Earth in Japan conducted a study on a technology called direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS) and its impact on global food access. The study aimed to find solutions for achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions while ensuring food security. DACCS is an innovative negative emission technology (NET) that captures carbon dioxide directly from the air and stores it. The researchers analyzed different scenarios and found that implementing DACCS could mitigate the negative effects on food access, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa, by reducing the increase in food expenditure and minimizing GDP loss associated with emission reduction efforts. In this scenario, DACCS would become a mainstream NET, replacing bioenergy with carbon capture and storage. Additionally, DACCS would enable the use of gas and oil without carbon capture in regions and sectors where emission reduction is challenging, helping to mitigate GDP loss. Overall, the study suggests that DACCS is a valuable option for achieving both net-zero emissions and favorable food access.
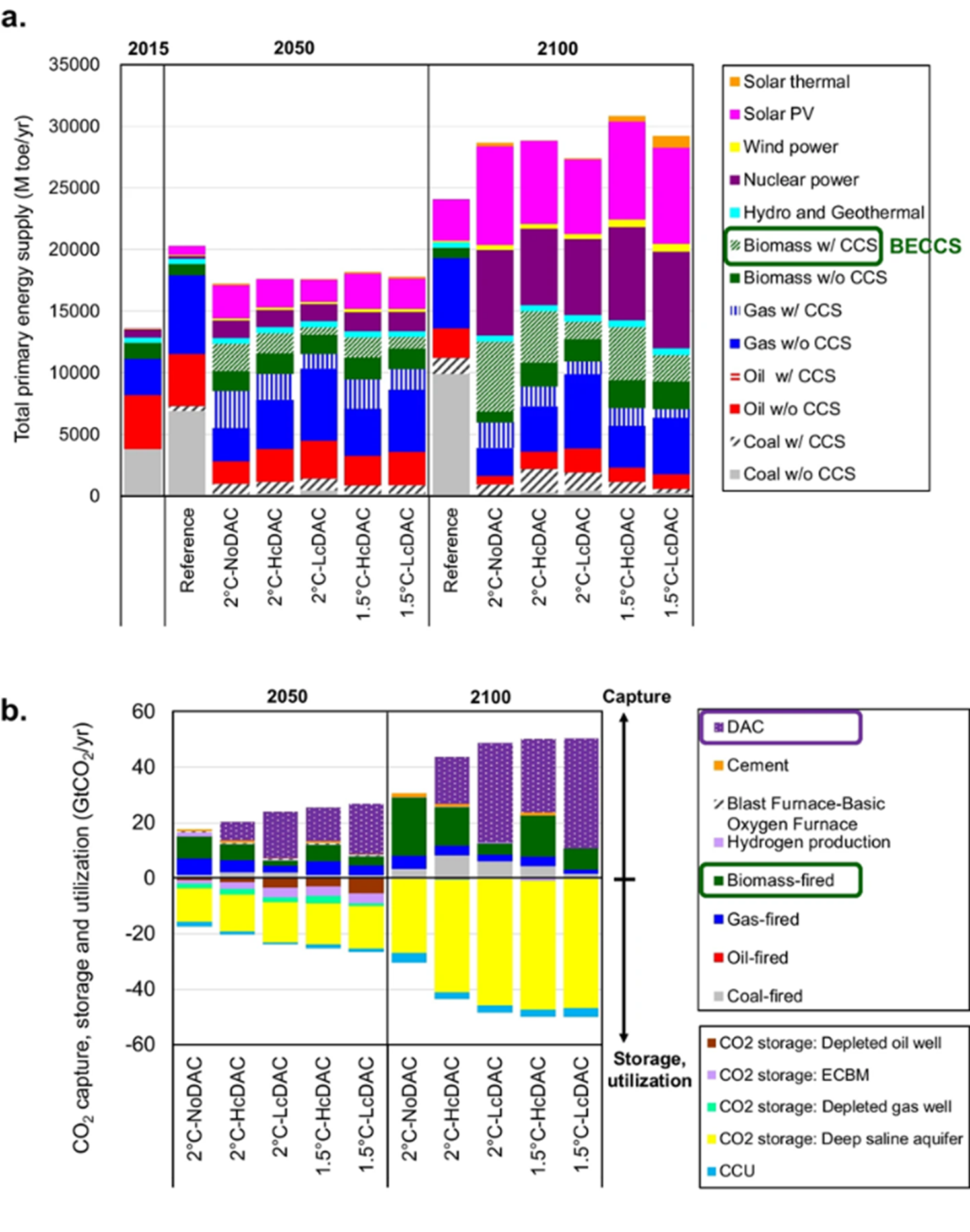
A Global total primary energy supply, and b global CO2 capture, storage, and utilization. “CCU” in b refers to the use of the captured CO2 for the production of synthetic methane, synthetic oil, etc. CO2 removal by afforestation (around 5 Gt CO2/ year in 2050 and almost zero in 2100 for all of the 2 °C and 1.5 °C scenarios) is not included in b





