Science of The Total Environment | March 1, 2023
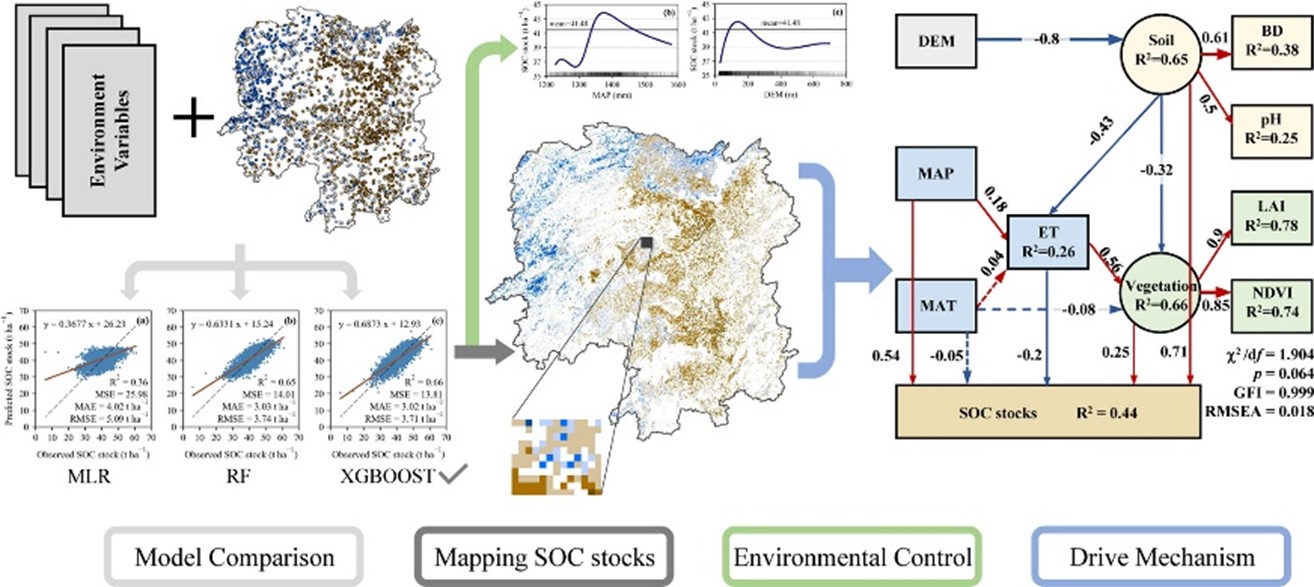
Soil organic carbon (SOC) is crucial for mitigating climate change by influencing CO2 levels. Researchers from China Agricultural University and University of Tasmania in Australia conducted a study to understand the factors influencing SOC in croplands. Using machine learning and observed soil samples from Hunan Province, China, they examined 16 environmental variables and their impact on SOC.
The results showed that the extreme gradient boosting (XGBOOST) model performed best, accurately predicting 66% of SOC variations. High SOC levels were found in low-altitude areas with sufficient water. Precipitation had a positive relationship with SOC, but with diminishing returns.
The study also used a structural equation model to uncover direct and indirect effects of environmental variables on SOC. Soil properties influenced by elevation had the most significant impact, while precipitation and elevation directly and indirectly affected SOC levels.
This research provides valuable insights into SOC dynamics and offers guidance for sustainable land management practices to enhance carbon sequestration in croplands. The findings contribute to our understanding of SOC and inform efforts to mitigate carbon loss in agricultural soils under climate emergency conditions.
Graphical abstract