September 12, 2023 | Scientific Reports |
Introduction: Crop residue cover (CRC) is a critical but understudied factor in agriculture's impact on both productivity and soil quality. Researchers from Sapienza University of Rome, University of Tabriz, Golestan University, the University of London, and Kansas State University have collaborated to investigate these effects. They employ a novel approach combining remote sensing and geospatial analysis to detect CRC and monitor its consequences on agriculture and soil characteristics.
The Study: The research team collected Landsat images and ground control points (GCPs) from 2013, 2015, and 2021. They harnessed the power of convolutional neural networks (CNN) to distinguish between areas with and without CRC. To assess the impact of CRC, they utilized the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from Landsat images in 2015, 2019, and 2022. Additionally, field observations were collected to evaluate how CRC affects soil fertility.
Key Findings: The CNN demonstrated impressive accuracy (>95%) in detecting CRC. The results suggest that CRC has a positive influence on agricultural productivity, as seen in increased vegetation density in the study areas between 2015 and 2022. Furthermore, CRC appears to enhance soil quality, indicated by changes in various chemical and physical characteristics. These improvements encompass parameters such as electrical conductivity (EC), pH, sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), bicarbonate (HCO3), potassium (K), and soil texture (silt, sand, and clay).
Conclusion: This study highlights the potential of an integrated approach that combines remote sensing and geospatial analysis to detect and evaluate the effects of CRC on agricultural productivity and soil fertility. The findings offer valuable insights for researchers and decision-makers in soil science, land management, and agriculture, demonstrating the significance of considering CRC in sustainable agricultural practices.
Read more: Monitoring the impacts of crop residue cover on agricultural productivity and soil chemical and physical characteristics
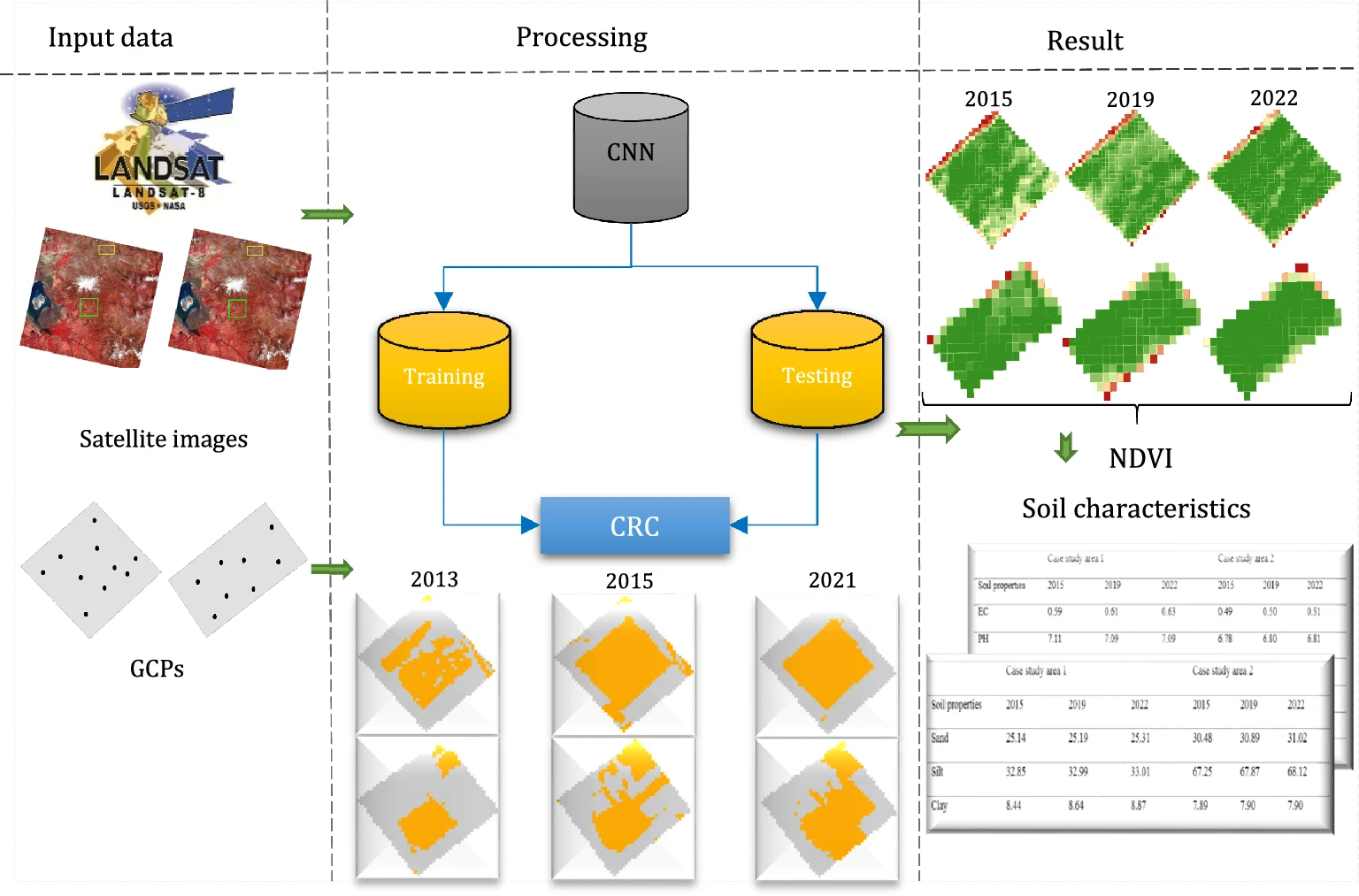
Fig. | An overview of the employed methodology to evaluate the effects of CRC on agricultural productivity and soil fertility.





