August 17, 2023 | Nature Food |
Introduction: The study conducted by the University of Minnesota, Colorado State University, Chongqing University, and other institutions in the US and China delves into the intricate connections between agricultural irrigation, climate change, and their impact on greenhouse gas emissions. These interrelated factors form a complex web that warrants closer examination.
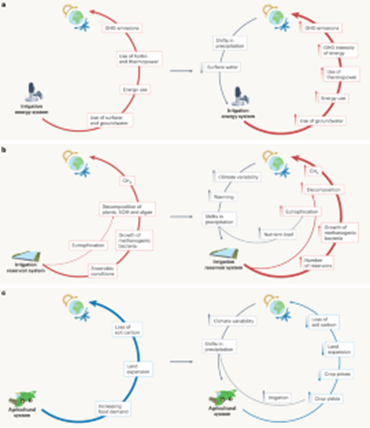
The Study: The research offers a comprehensive scoping review, bridging insights from diverse fields to shed light on the interactions between irrigation and climate. It explores the multifaceted ways in which agricultural irrigation contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, either directly from soils or indirectly through energy consumption and infrastructure development. Simultaneously, the study highlights how climate change influences irrigation practices, affecting water availability, demand, and the environmental footprint of irrigation energy.
Key Findings: The scoping review emphasizes the growing significance of climate change as a driving force behind future expansions in irrigation. Additionally, it uncovers positive feedback loops in this relationship, where climate change and irrigation practices reinforce each other, potentially exacerbating environmental impacts.
Conclusion: The study underscores the pressing need to embrace sustainable irrigation practices, especially in regions where these strong, positive feedback loops are prominent. By understanding the complex interplay between irrigation, climate, and greenhouse gas emissions, policymakers and researchers can work towards mitigating the environmental effects of agriculture and ensuring a more sustainable future.
Read more: Sustainable irrigation and climate feedbacks