September 1, 2023 | Science of The Total Environment |
Introduction: This collaborative study, involving researchers from AgResearch Ltd in New Zealand, INIA in Chile, Aarhus University in Denmark, ADAS UK, and ATB Germany, delves into the intricate factors influencing ammonia (NH3) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions associated with livestock manure management. These emissions play a significant role in both air quality and climate change, underscoring the need to better understand their underlying drivers.
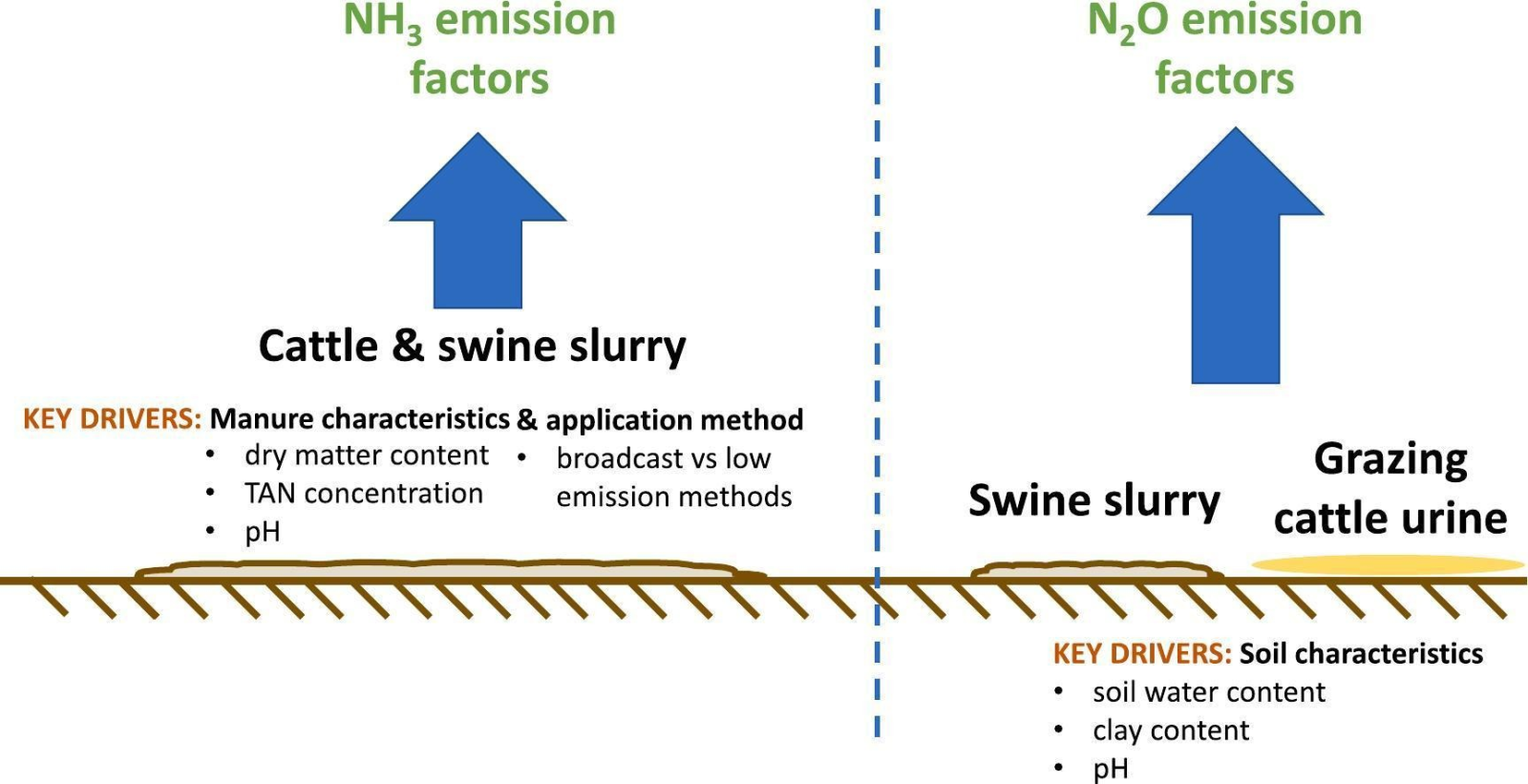
The Study: By analyzing data from the DATAMAN ("DATAbase for MANaging greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions factors") database, the research focuses on identifying the key factors affecting NH3 emission factors (EFs) for cattle and swine manure applied to land, as well as N2O EFs for the same scenarios. Additionally, it examines the factors impacting cattle urine, dung, and sheep urine emissions during grazing.
Key Findings: The study reveals that several factors significantly influence NH3 EFs, including slurry dry matter (DM) content, total ammoniacal nitrogen (TAN) concentration, and the method of application. These findings can explain a substantial portion of the variance in NH3 EFs, making them vital focal points for mitigation strategies. In contrast, identifying key factors affecting N2O EFs posed a more complex challenge due to the multitude of variables influencing microbial processes and soil properties related to N2O production and emissions. Nonetheless, soil-related factors such as soil water content, pH, and clay content emerged as significant drivers.
Conclusion: This comprehensive analysis contributes to an enhanced understanding of NH3 and N2O EFs, making way for their incorporation into emission models. As more studies add to this knowledge base, it will continue to refine our understanding of the processes governing these emissions and, in turn, facilitate more effective mitigation strategies for air quality and climate change management.
Read more: Influence of key factors on ammonia and nitrous oxide emission factors for excreta deposited by livestock and land-applied manure