June 10, 2023 | Science of The Total Environment |
Subsurface application (SA) of nitrogenous fertilizers offers a promising solution to address climate change and ensure food security. Researchers from Gyeongsang National University, Korea, and Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Bangladesh, conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis to assess the impact of SA technology on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, crop yield, nitrogen uptake (NU), and soil nitrogen levels.
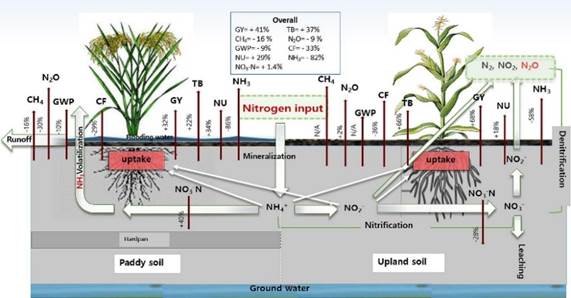
Findings from 40 peer-reviewed studies reveal that SA technology significantly boosts rice yields by 32% and crop yield in upland systems by 62% compared to surface application of nitrogen (N). Notably, the greatest yield increases were observed at lower N input rates in rice paddies and medium N input rates in upland systems, indicating the influence of soil moisture on SA effectiveness.
SA treatments lead to substantial NU increases, with 34% in rice paddies and 18% in upland systems, while curbing ammonia (NH3) emissions and carbon footprint (CF) by 29% and 36% respectively. Additionally, SA demonstrates significant reductions in methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions, resulting in a 10% decrease in global warming potential (GWP) during paddy cultivation.
This meta-analysis highlights the dual benefits of SA technology: mitigating climate change by reducing GHG emissions and enhancing food security through improved crop yield and nutrient uptake. It underscores the potential of SA as a sustainable agricultural practice for a resilient future.
Graphical abstract