May 20 2023 | Science of The Total Environment |
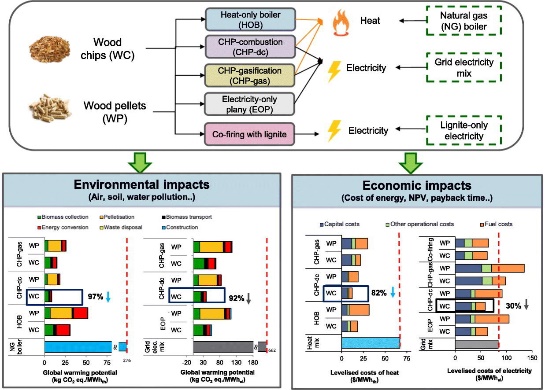
A recent study conducted by The University of Manchester focuses on the potential of using forest residues as a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels for energy generation in Turkey. Forest residues, such as wood chips and wood pellets, are abundant and inexpensive feedstock that can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy security. The study evaluates the environmental and economic sustainability of different energy conversion options using forest residues, including direct combustion for heat and electricity, gasification for combined heat and power (CHP), and co-firing with lignite. The findings indicate that direct combustion of wood chips for cogeneration of heat and power has the lowest environmental impact and levelized costs for both heat and electricity generation. Energy derived from forest residues has the potential to significantly reduce climate change impact and reliance on fossil fuels, although it may increase some other impacts like terrestrial ecotoxicity. The study also highlights the economic feasibility of bioenergy plants, with some types generating net profits and offering cost savings compared to grid electricity and natural gas. By utilizing Turkey's available forest residues, the country could reduce greenhouse gas emissions and save on fossil fuel import costs.
Graphical abstract