September 26, 2023 | Nature Reviews Earth & Environment |
Introduction: Rice paddies supply stable food to half of the world's population but contribute about 48% of GHG emissions from croplands. Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology and Ecology in Southern China, Nanjing and University of Exeter, UK collaborated on reviewing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, mainly methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), from rice fields and their impact on climate change.
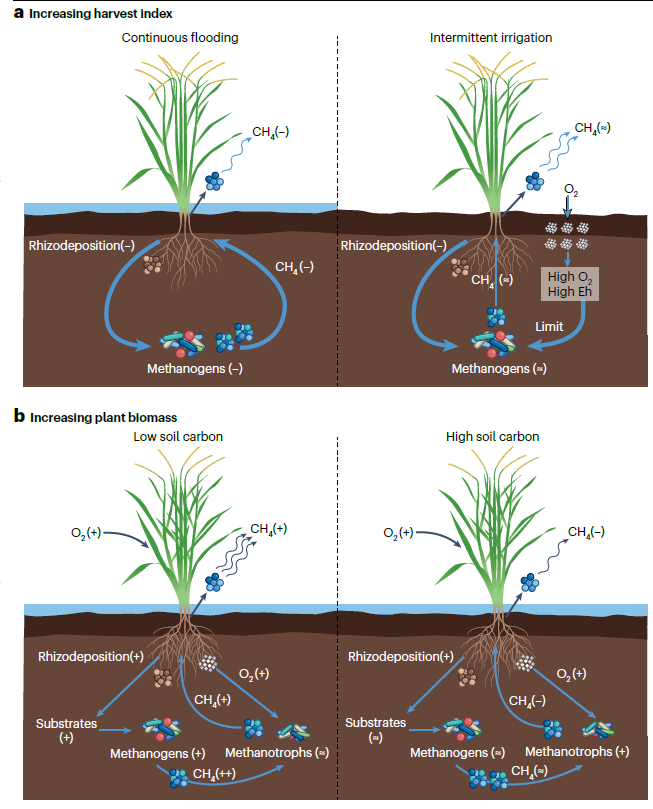
Key findings: On average, each hectare emits approximately 7,870 kilograms of carbon dioxide equivalent per year, with CH4 accounting for 94%. Emissions vary due to different management practices; for example, adding organic matter and continuous flooding increase CH4, while nitrogen fertilizer application drives N2O emissions. Although current emission trends are uncertain, future projections suggest increased CH4 emissions due to elevated CO2 and warming.
Conclusion: The review study proposes integrated agronomic strategies, such as selecting new rice varieties, reducing continuous flooding, and removing straw, which could reduce emissions by 24%, 44%, and 46%, respectively. However, optimizing these approaches based on seasonal CH4 emission patterns is crucial, highlighting the need for improved measurement and reduced uncertainty in global GHG estimates, especially in low latitudes.
Fig. 1 | CH4 emissions as affected by breeding strategies to increase rice yield.
Fig. 2 | Potential mitigation strategies