The European Green Deal Improves the Sustainability of Food Systems but Has Uneven Economic Impacts on Consumers and Farmers
October 7, 2023 | Communications Earth & Environment |
Introduction: EU established the policy program called The European Green Deal in 2019, aiming to create a fair, healthy, and environmentally friendly food system. To assess the impacts of this initiative, a partial equilibrium economic model was developed by France's National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE). The model focuses on three main strategies: reducing chemical inputs in agriculture, minimizing post-harvest losses, and promoting healthier diets with fewer animal-based products.
Key findings: The study emphasizes that achieving significant improvements in climate, biodiversity, and nutrition necessitates the simultaneous implementation of all three measures. This integrated approach could result in a 20% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from food consumption and a 40–50% decrease in biodiversity damage. Consumers benefit economically through lower food expenses, but livestock producers experience declines in quantity and price. Positive impacts on revenues for food/feed field crop producers depend on the balance between increased food consumption and reduced feed consumption.
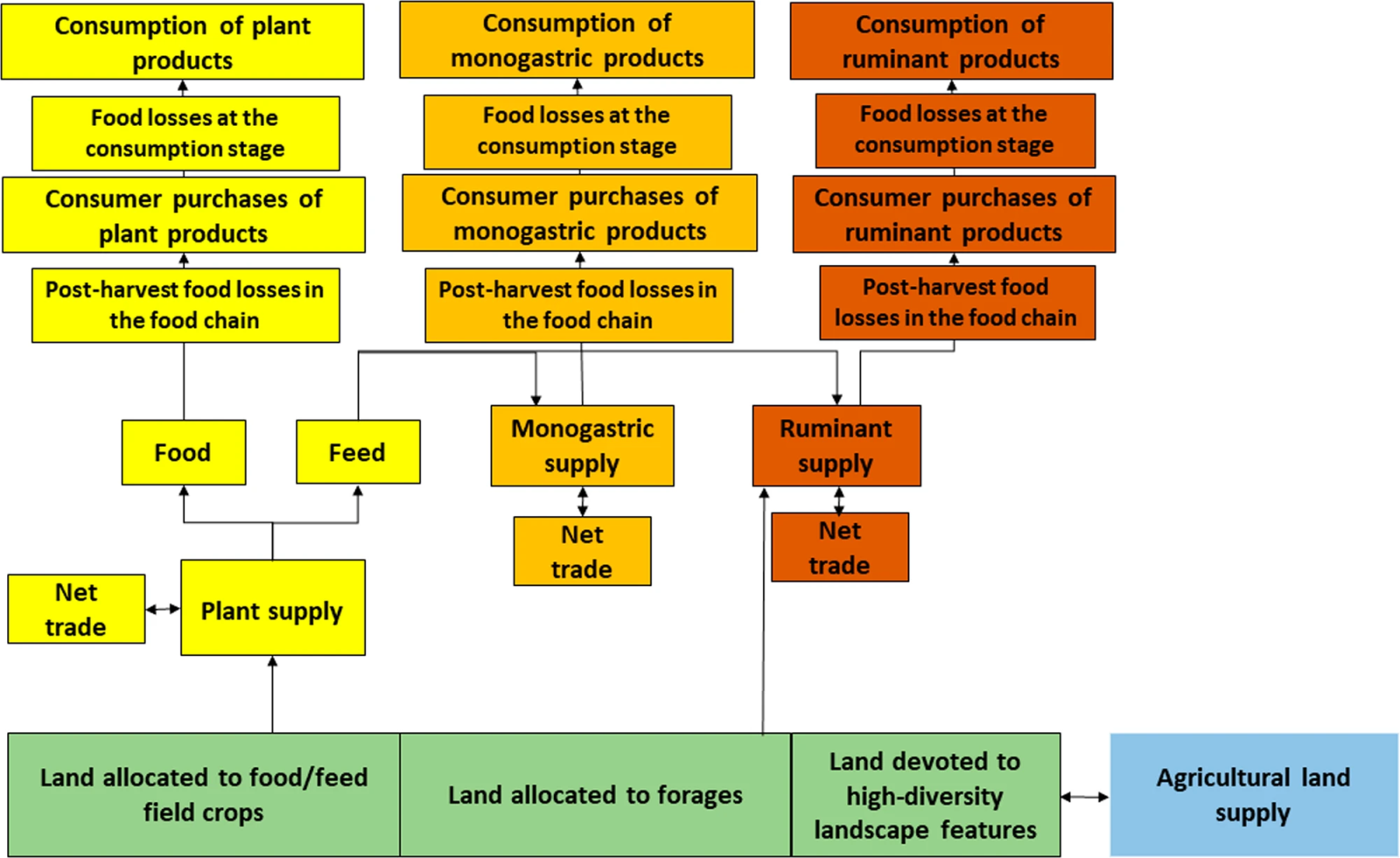
Fig. | Structure of the partial equilibrium economic model.
Viewed Articles
October 7, 2023 |  Communications Earth & Environment |  Introduction: EU established the policy program called The European Green Deal in 2019, aiming to create a fair, healthy, and environmentally f
Read More
June 15, 2025 | Global Transitions |  Introduction: A study from the Sasin School of Management at Chulalongkorn University in Thailand examines systemic weaknesses in voluntary carbon markets (VCMs)
February 25, 2024 | Journal of Cleaner Production |  Introduction: Place-based agricultural policies are increasingly adopted to balance food security with environmental sustainability, yet their impa
September, 2025 | Environmental and Sustainability Indicators |  Introduction: Carbon pricing and related climate policies are increasingly positioned as core levers for decarbonizing food systems, ye
February 14, 2024 | Journal of Environmental Management |  Introduction: A research team from the University of Bologna and the University of Urbino Carlo Bo in Italy conducts a systematic mapping stu
October 12, 2020 | Nature Sustainability |  Introduction: An international research team led by researchers from the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), in collaboration with multila






