September 28, 2023 | Nature Communications |
Introduction: Despite the growing challenge of land scarcity for agriculture, there is a significant global trend of cropland abandonment. Researchers from National University of Singapore has identified 101 million hectares of potential cropland that was abadoned between 1992 and 2020 from time series recently published by ESA Climate Change Initiatives (ESA-CCI), and explores the potential and trade-offs associated with reusing abandoned cropland for both food security and climate change mitigation spatially-explicit modeling and scenario analysis.
Key findings: The modeling results suggest that this abandoned cropland could simultaneously contribute to food production potential (ranging from 29 to 363 Peta-calories yr-1) and net climate change mitigation potential (ranging from 290 to 1,066 MtCO2 yr-1), depending on land-use suitability and allocation strategies. The findings emphasize the importance of spatial prioritization to maximize the achievable potential of abandoned cropland. The study also presents various approaches to further enhance these potentials.
Conclusion: Ultimately, this research provides valuable insights into the possibilities of repurposing abandoned cropland for sustainable land management, offering a timely perspective to support both food security and climate goals.
Read more: The neglected role of abandoned cropland in supporting both food security and climate change mitigation
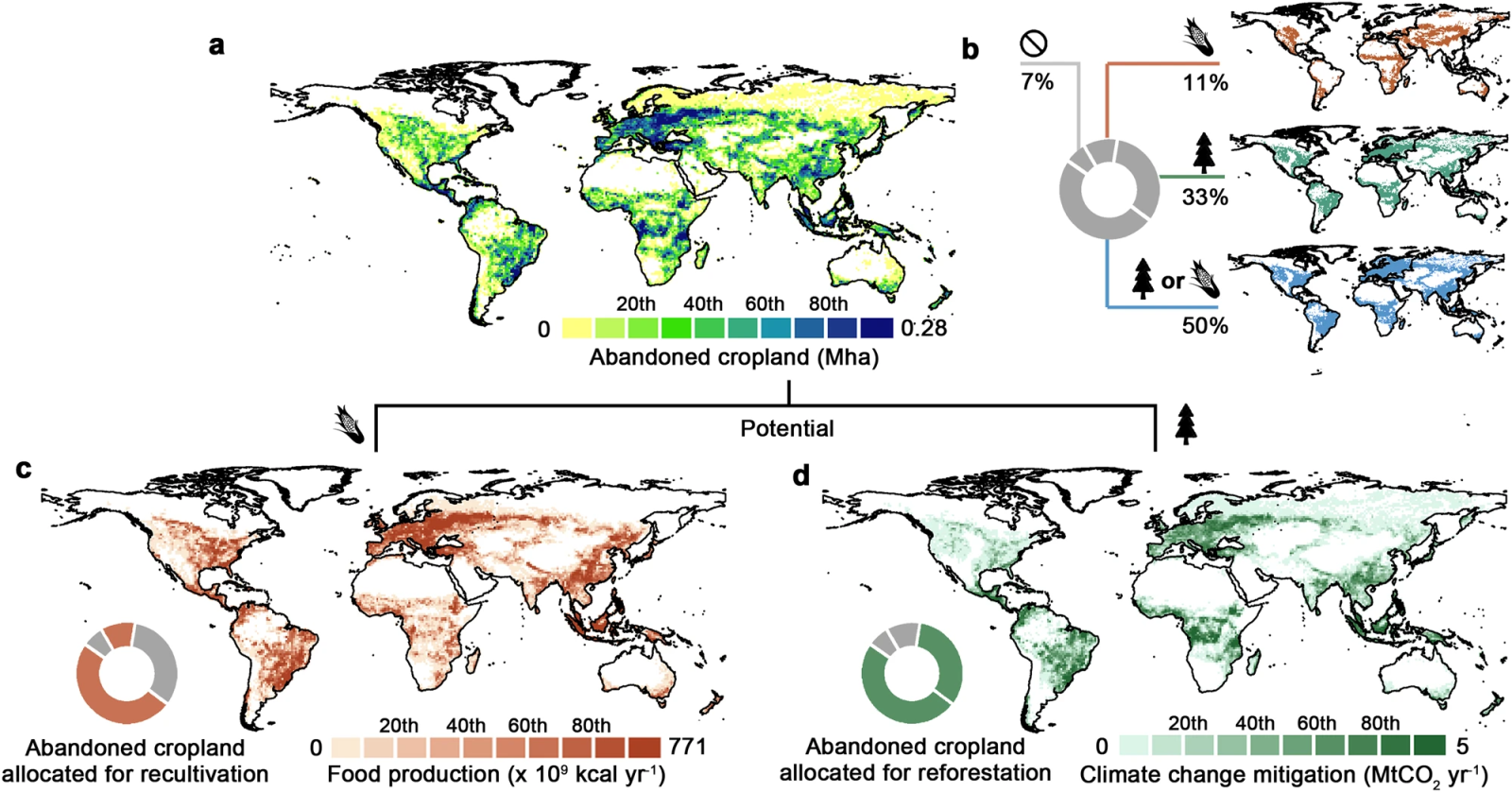
Fig. | Global abandoned cropland: extent, suitability, and potential.





