A redistribution of nitrogen fertilizer across global croplands can help achieve food security within environmental boundaries
September 28, 2023 | Communications Earth & Environment |
Introduction: Producing enough food for a growing global population while reducing environmental pollution and climate impact is a major challenge. From simulating global cereal cropping systems, the researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) in Germany proposed a strategy of optimizing fertilizer application across global croplands of major cereal crops such as maize, wheat, and rice.
Key findings: The current cereal production levels could be maintained with a 32% reduction in total global fertilizer use. Alternatively, cereal production could be increased by 15% with current nitrogen fertilizer levels. This redistribution approach not only ensures food production but also leads to substantial reductions in nitrogen pollution. Moreover, a more equitable distribution of nitrogen fertilizer across global croplands could reduce pollution on in heavily fertilized regions such as East Asia, and allow areas like Sub-Saharan Africa to move towards self-sufficiency.
Read more: A redistribution of nitrogen fertiliser across global croplands can help achieve food security within environmental boundaries
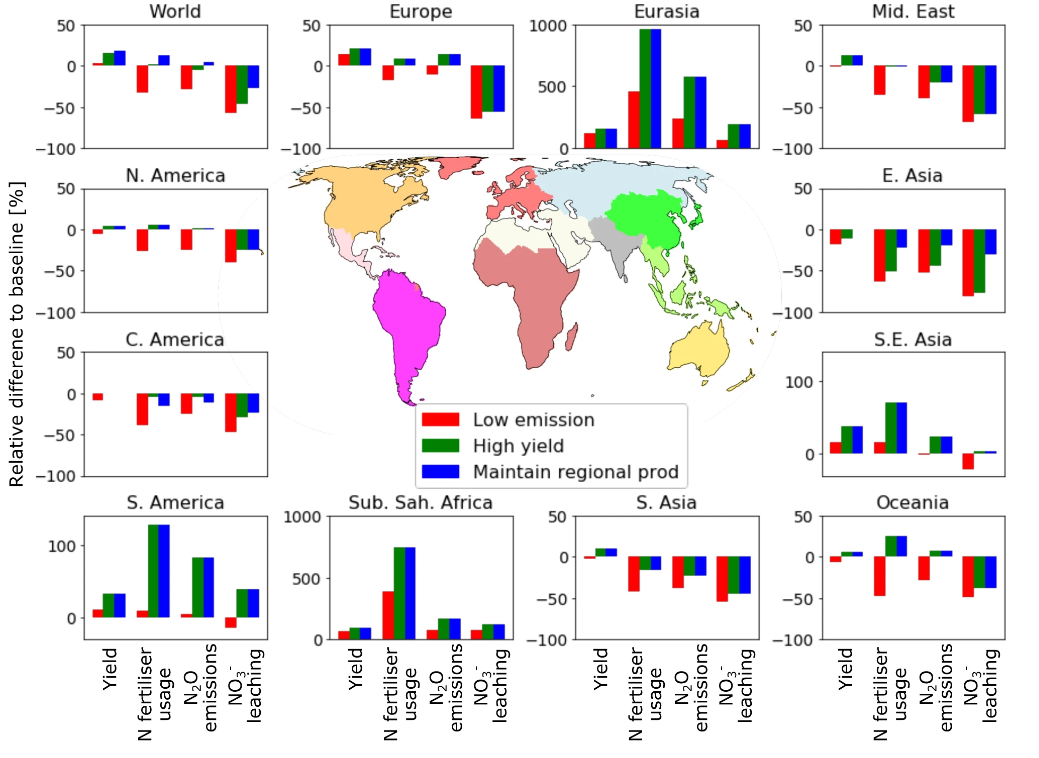
Fig. | Regional changes in cereal yield, N-fertiliser usage, N2O emissions and NO3− leaching. Changes are shown relative to the baseline scenario.
Viewed Articles
September 28, 2023 | Communications Earth & Environment |Â Â Introduction: Producing enough food for a growing global population while reducing environmental pollution and climate impact is a major chal
Read More
June 20, 2021 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source | Introduction: Researchers from the University of Michigan (USA) analyzed the lifecycle GHG emissions of perishable foods—vegetables, fruits, me
March 13, 2023 | Nature Food | Source | Â Introduction: Food loss and waste (FLW) are major contributors to global GHG emissions, yet their full impact across the food system has been underexplored. A
September 25, 2022 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Source |  Introduction: Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) exacerbate the global food system’s failure by driving environmental harm, undermining nutriti
January 15, 2022 | Atmosphere | Source |Â Introduction: Livestock both drives and suffers from climate change, contributing 14.5% of global GHG emissions while facing growing climate-induced stress. Re
November 12, 2024 | Nature Food | Source |Â Â Introduction: While nitrogen (N) inputs are essential for crop productivity, N losses from croplands contribute to major environmental issues, including cli





