October 20, 2023 | One Earth |
Introduction: The Earth's land ecosystem absorbs around 30% of the carbon dioxide emitted by human activities annually, playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change. However, the continuing effectiveness of this carbon sink will depend on water availability and other climate conditions. Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences used data from CMIP6 to model the impact of droughts on vegetation productivity and associated carbon sink.
Key findings: When comparing historical data (1851–2000) to future scenarios at the end of the century (2076–2100), global mean reductions in vegetation productivity due to droughts are estimated to rise by 2.3 times under a sustainable development scenario and 3.5 times under a fossil-fueled development scenario. These drought-induced productivity losses are anticipated to surpass the predicted gains in productivity from increased carbon dioxide "fertilization," especially in cropland. The modeling results suggest that the intensification droughts in a warmer future could pose risks to global food security and potentially shift the terrestrial ecosystem from being a carbon sink to becoming a carbon source.
Read more: Increasing meteorological drought under climate change reduces terrestrial ecosystem productivity and carbon storage
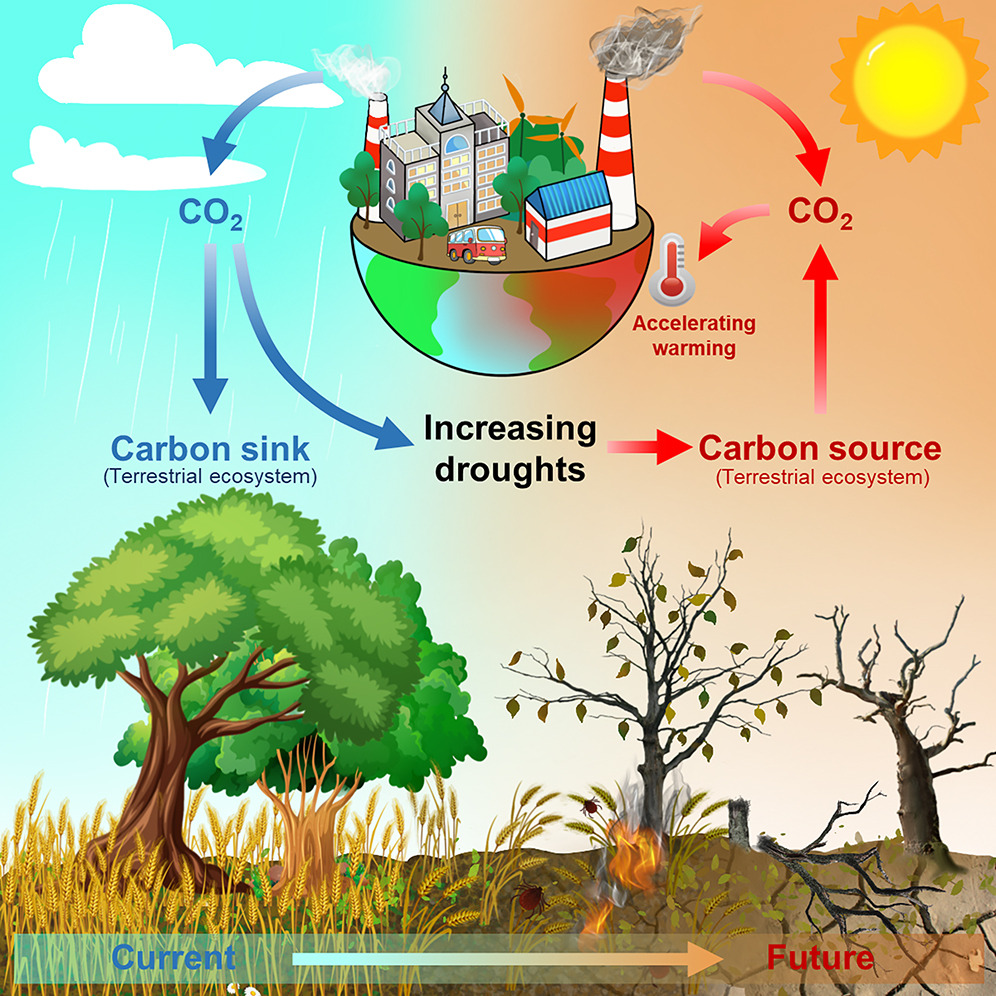
Fig. | Graphical Extract.





